Structure of optical fiber pdf
Optical Fiber Structure . In the initial stage, glass or silica material was utilised to create an optical fiber. Advancements in technology though, called for the use of plastic material to make the optical fiber.
PDF Graphical abstract Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (BOTDR) for concrete structure health monitoring Abstract An innovative technique based on optical fibre sensing that allows
DH laser structure provides optical confinement in the vertical direction through the refractive index step at the heterojunction interfaces, but lasing takes place across the whole width of the device.
core structure of optical cables In common optical cable designs, one or more optical fiber conductors are combined in a given ıstructure and form the heart of the cable, called the cable core.
Optical Fiber Structures The principles explained in the preceding section apply to optical fiber with a “step index” (SI) structure. This is the structure used for most POFs, including those manufactured by Mitsubishi Rayon.
The fiber gyroscope is based on a fiber-optic realiza- strain and/or temperature sensors for load and condition moni- tion of the Sagnac interferometer—which was first demonstrat- toring, particularly in carbon fiber composite structures.
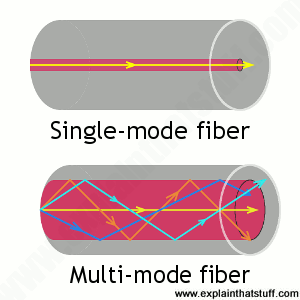
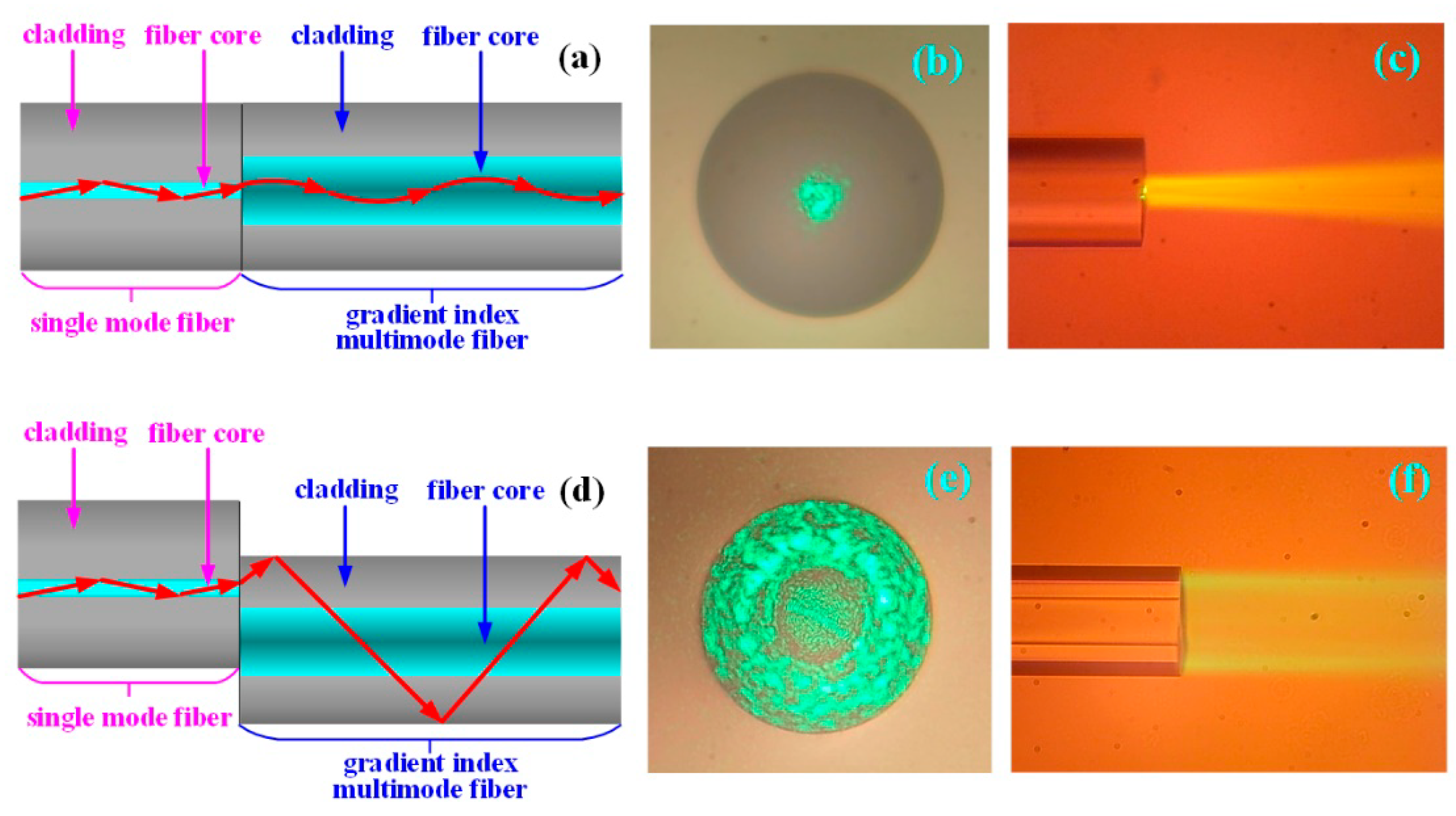
multi-mode fiber approximately agree with the predictions of geometric optics, if the fiber core is large enough to support more than a few modes. Figure 3: The structure of a typical single-mode fiber.
The installation of optical fiber cable requires expertise, experience and individual judgments about the methods and procedures appropriate to any particular situation.
mode optical fibers light propagates along one path that is nearly parallel to the fiber axis (Fig.1.10). The detailed analysis of light propagation based on the electrodynamic analysis will be provided in Chapter 1.4. We say that light wave propagates as a single mode, so-called fundamental mode, if there exists only one spatial electromagnetic field structure inside the optical fiber. Fig.1
An optical fiber module identification based on RFID technology, characterized in that: said housing includes structure identification, fiber tail sleeve and an electronic identification device, an optical fiber connector ferrule end of the housing, the electronic identification device is mounted within the housing or ferrule fiber …
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) Definition Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a fiber-optic transmission technique that employs light wavelengths to transmit data parallel-by-bit or
Optical fiber is a type of cabling technology that uses light to carry voice and data communications (telecommunications) over distances both great and small.
Basic structure of an optical fiber tpub.com
Structure of fiber optics cable Home
Optical fibers: structures, waveguiding, Optical f fabrication and optical cable. Chapter 2 Optical Fibers ¾What is the structure of an optical fiber ? ¾How does light propagate along a fiber ? ¾Of what materials are fibers made ? ¾How is the fiber fabricated ? ¾How are fibers incorporated into cable structures ? ¾What is the signal loss or attenuation mechanism in a fiber ? ¾Why and to
Structure of Optical Fiber The optical fiber is made up of two concentric cylindrical strands of silica surrounded by a plastic coating. The center most silica strand is the cone of the fiber with a refractive index 1 of approximately 1.48.
couple an optical fiber with a laser or a photodiode Connecting a light source or a receiver to an optical fiber requires to align precisely the formers to the latter.
II.2 Optical Fiber/Cable In this section, we discuss the structure and properties of an optical fiber, how it guides light, and how it is cabled for protection.
Introduction to Fibre Optics. The field of fibre optics communications has exploded over the past two decades. Fibre is an integral part of modern day communication infrastucture and can be found along roads, in buildings, hospitals and machinary.
7 2. Fundamentals of fiber optics The Internet, smart phones, PAD’s and eReaders are a way of life in modern society. All of these technologies rely on optical networks.
The basic structure of an optical fiber consists of three parts; the core, the cladding, and the coating or buffer. The basic structure of an optical fiber is shown in figure 2-9. The core is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material. Dielectric material conducts no
Designing and Managing Fiber Optic Networks G The growing demand for fiber optic networks not only creates the need for more designers, it also creates the need for an information system to manage the infrastructure. The integration of engineering design and visualization tools with network data asset management is an ideal application for a geospatially enabled infrastructure management
An optical fiber magnetic field sensor based on the single-mode-multimode-single-mode (SMS) structure and magnetic fluid (MF) is proposed and demonstrated. By using a piece of no-core fiber …
20/07/2017 · An optical fiber is a flexible and transparent fibre, made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly more than that of a human hair (including outer coating, its diameter is 0.25
optical design of the fiber (e.g. interfacial structure at the core-clad interface, uniformity of core-clad structure along fiber length). Thus, the control of material structure (through composition, material processing, and fiber fabrication controls) is the primary means to reduce attenuation in . 2 The authors would like to acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation through
An optical fiber is a cylindrical structure that transports electromagnetic waves in the infrared or visible bands of electromagnetic spectrum. In practice optical fibers are highly
Optical fibers are characterized by their structure and by their properties of transmission. Basically, optical fibers are classified into two types. The first type is single mode fibers. The second type is multimode fibers. As each name implies, optical fibers are classified by the number of modes that propagate along the fiber. As previously
Considerations on the physical-chemical and structural features of optical fibres 129 Fig. 2. The Growth of Optical Fiber Transmission Capacity [4]

Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing Technology for Social Infrastructure Monitoring Kengo Koizumi Hitoshi Murai Aging of the social infrastructure developed during the high economic growth period is now a major problem, and construction of monitoring systems has become an urgent task. In particular, health-monitoring tests using various sensors are being conducted to prevent collapse of bridges
Module 2 – Optical Fiber Materials . Dr. B.G. Potter . Professor, Material Science and Engineering Dept, University of Arizona . Dr. B.G.Potter is a Professor of Material Science and Engineering in the University of Arizona. Research activity within Dr. Potter’s group is centered on the synthesis and study of glass, ceramic, and molecular hybrid materials for photonic and electronic
Light-emitting diodes for optical communication 471 changes in these parameters cause the instability of transfer coefficients of optical fiber lines [5,6].
optical fibers and fiber-optic communications10 .7 FIGURE 5 Bessel functions J m ( r ) for m 5 0 , 1 , and 2 . The step-index fiber of circular symmetry is a particularly important case , because
SECTION 7: MULTIPLEXING TECHNIQUES, NETWORKS, and DEVICES 1. BASIC NETWORK TOPOLOGIES 1. Bus – Backplane user 1 user 2 user 3. . . . • Issues of contention for accessing the bus 2. RING user 1 user 2 user 3 user 4 user 5 user 6 user 7 • Individual passive optical tap is required for each node. • Similar to BUS Network in this regard. • Approach becomes intolerable for large node
Structure of the optical fiber cable. Core and cladding are typically made of glass or plastic. Most important specification of the core is the index of refraction which is the value for light bending passing through the material and for the speed of that light could travel through material with.
CARACTERIZATION OF THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF OPTICAL
optical fibers installed on the structure to be monitored (Figure 2). The measurement fiber is pre-tensioned and mechanically coupled to the structure at two anchorage points in order to follow its deformations, while the ref-erence fiber is free and acts as temperature reference. Both fibers are installed inside the same pipe and the measurement basis can be chosen between 200mm and 10m. …
Optical fibers Modes Configurations and types: An optical fiber is a dielectric waveguide that operates at optical frequencies. It confines electromagnetic energy in the form of light to within its surfaces and guides the light in a direction parallel to its axis. The transmission properties of an optical waveguide are dictated by its structural characteristics, which have a major effect in
Synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) and synchronous optical network (SONET) refer to a group of fiber-optic transmission rates that can transport digital signals with different capacities. – woolworths casual jobs application forms Guide An educational resource published by Communications Specialties, Inc.. Introduction to Fiber Optics The equipment, tools and cabling that comprise a fiber optic link, how they work and their advantages over traditional copper. commspecial.com. edu Guide Communications Specialties, Inc. is committed to increased education and knowledge in the Pro A/V and Broadcast industries. We hope …
Optical fiber structure & characteristics At the heart of this technology is the optical fiber itself — a hair-thin cylindrical filament made of glass that is able to guide light through itself by confining it within regions having different optical indices of refraction.
Optic Fiber Structure Optical fibers consist of a pure glass core surrounded by multiple layers. The first layer is a reflective cladding, which acts like a long, flexible mirror, reflecting light along the length of …
An optical fiber is a single, hair-fine filament drawn from molten silica glass. These fibers are replacing metal wire as the transmission medium in high-speed, high-capacity communications systems that convert information into light, which is then transmitted via fiber optic cable.
1. Optical fiber structure Optical fiber is information-carrying medium made with silica-based glass. It consists of two regions : the core and the cladding.
enclose the fiber, but this design is difficult to achieve in practice with DSSCs. An improved design takes advantage of the rectangular optical fiber geometry.
1 Design and optimization of tapered structure of near-field fiber probe based on FDTD simulation H. NAKAMURA and T. SATO Theory and Computer Simulation Center, National Institute for Fusion Science, 322-6 Oroshi-cho,
Fig. 1 Schematic structure of an optical fiber (left) ; schematic refractive index profile (right). One of the first applications of glass optical fibers was fiberscope. However the poor
The Structure and Physics of an Optical Fiber The optical fi bers used in communications have a very simple structure. They consist of two sections: the glass core and the cladding layer (Figure 5.1). The core is a cylindrical structure, and the cladding is a cylinder without a core. Core and cladding have different refractive indices, with the core having a refractive index, n 1, which is
The optical cable structure protects optical fibers from environmental damage. Cable structure includes buffers, strength members, and jackets. Many factors influence the design of fiber-optic cables. The cable design relates to the intended application of the cable. Properly designed optical cables perform the following functions:
Fibers . 2014, 2 . 2 . Chemical optical fiber sensors for the detection of polluting substances in water, soil, and air, such as the biological sensors, optimized for medicine applications, have attracted noticeable interest
The optical properties of the fiber material (which is usually fused silica), including its attenuation and the effects of material, modal, and waveguide dispersion on the transmission of light pulses, are discussed in Sec. 8.3.
Alibaba.com offers 878 structure of optical fiber products. About 1% of these are steel structures, 1% are warehouses, and 1% are metal building materials. A wide variety of structure of optical fiber options are available to you, such as steel workshop, steel fabricated house.
Although optical fiber has superior signal capacity and immunity to electromagnetic inter- ference, there is one basic aspect where fiber lags behind copper cables and this is the signal loss incurred if bent around tight corners.
Chapter 2 Optical fibers structures waveguiding Optical
There are three types of fiber optic cable: single mode, multimode and plastic optical fiber (POF). Single Mode cable is a single stand of glass fiber with a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns. (One micron is 1/250th the width of a human hair.)
Basics and Features of High-Power Fiber Laser in laser processing field. Fujikura has grown up high-power fiber laser technologies on the basis of its proprietary optical fiber related technologies, and one of the milestones is described in “special issue on fiber laser” of this Fujikura Technical Review. As an introdction of the issue, this report reviews structural features of high
Fiber optics is being used in diverse applications such as cold lighting in museums, construction of smart civil structures, and networking for communication. Among many issues associated with day-to-day handling of optical fibers, a fiber optic technician may have to solve problems regarding joining of optical fibers, location of fiber breaks, and fiber end preparation. The field of fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible filament of very clear glass capable of carrying information in the form of light. Optical fibers are hair-thin structures created by forming pre-forms, which are glass rods drawn into fine threads of glass protected by a plastic coating. Fiber manufacturers use various vapor deposition processes to make the pre-forms. The fibers drawn from these pre-forms are
6/27/89 optical fiber sensors and signal processing for intelligent structure monitoring nasa grant nag-1-895 july 1989 prepared for: dr. robert rogowski
structures Optical fibre cable Recommendations for different environments L.10: Optical fibre cables for duct and tunnel application This Recommendation describes characteristics, constructions and test methods for optical fibre cables for duct and tunnel application. L.26: Optical fibre cables for aerial application This Recommendation describes characteristics, constructions and test methods
A connecting structure of an optical fiber to an optical waveguide includes a circular cylindrical holder having a bore with a circular cross-section communicating one end thereof to the other. The protecting layer removal end of the optical fiber is inserted into the bore. An end plane of the protecting layer removal end and a side plane of
CORE STRUCTURE OF OPTICAL FIBER CABLES focabex.com
Optical Sources for Fiber Optic Communication Randhir
Since the breakthrough of optical fibers in communication, awarded with a Nobel prize in 2009 1, a series of fiber-based applications grew alongside. Nowadays, fibers are a necessity in laser surgeries 2 , as well as in coherent X-ray generation 3 , 4 , guided-sound 5 and supercontinuum 6 .
Compatibility of Low Bend Singlemode Fibers

US5671316A Connecting structure of optical fiber to
State of the Art in Fiber Optic Sensing Technology and EU
OPTICAL FIBER COUPLING STRUCTURE satt-technologies.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optic_fiber
Design and Fabrication of an Optical Fiber Made of Water
jelly yarn bracelet instructions – Optical Fiber Cable DCC Cables
(PDF) Distributed optical fibre strain sensing of


Optical fiber Structures Optical Fiber Waveguide
Module 2 Optical Fiber Materials
structure of optical fiber Alibaba
CHAPTER 10 OPTICAL FIBERS AND FIBER- OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS
An optical fiber is a cylindrical structure that transports electromagnetic waves in the infrared or visible bands of electromagnetic spectrum. In practice optical fibers are highly
An optical fiber is a flexible filament of very clear glass capable of carrying information in the form of light. Optical fibers are hair-thin structures created by forming pre-forms, which are glass rods drawn into fine threads of glass protected by a plastic coating. Fiber manufacturers use various vapor deposition processes to make the pre-forms. The fibers drawn from these pre-forms are
structures Optical fibre cable Recommendations for different environments L.10: Optical fibre cables for duct and tunnel application This Recommendation describes characteristics, constructions and test methods for optical fibre cables for duct and tunnel application. L.26: Optical fibre cables for aerial application This Recommendation describes characteristics, constructions and test methods
Optical fiber is a type of cabling technology that uses light to carry voice and data communications (telecommunications) over distances both great and small.
The fiber gyroscope is based on a fiber-optic realiza- strain and/or temperature sensors for load and condition moni- tion of the Sagnac interferometer—which was first demonstrat- toring, particularly in carbon fiber composite structures.
Introduction to Fibre Optics. The field of fibre optics communications has exploded over the past two decades. Fibre is an integral part of modern day communication infrastucture and can be found along roads, in buildings, hospitals and machinary.
Fibers . 2014, 2 . 2 . Chemical optical fiber sensors for the detection of polluting substances in water, soil, and air, such as the biological sensors, optimized for medicine applications, have attracted noticeable interest
CARACTERIZATION OF THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF OPTICAL
Basic Structure of an Optical Fiber tpub.com
Fiber Optical Fiber Sensor