Pulse broadening in graded index fiber pdf
Numerical Analysis of Pulse Broadening in Graded Index Optical Fibers Article (PDF Available) in IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 29(4):348 – 352 · May 1981 with 611 Reads
The pulse broadening of di erent mode of waves is intermodal dispersion. The intermodal dispersion of step-index ber The fastest wave is the wave along the center ( tp the normal is 90 o )
Optical Fibers Evolution of fiber optic system – Element of an optical fiber transmission link – Ray optics – Optical fiber modes and configurations – Mode theory of circular waveguides – Overview of modes – Key modal concepts – Linearly polarized modes – Single mode fibers – Graded index fiber structure.
Abstract: Minimum pulse broadening of multimode graded-index fibers is investigated theoretically. Exact solutions of the rms pulse-width σ for a fiber with a power-law index profile is obtained by using the integral expression of group delay time based the multilayer approximation.
The WKB analysis is extended to take into account the discontinuity in index profile shape that occurs at the core-cladding boundary of graded-index optical waveguides. The presence of the cladding introduces a large correction to the delay times of the highest 5% of the guided modes and greatly increases the predicted rms pulse broadening of a parabolic profile fiber. Using a model of
It is not really difficult to calculate the pulse broadening effect: where a 200-fs pulse runs through 50 cm of a step-index fiber. The spatial profile of the input pulse is a Gaussian, but it is not perfectly aligned to the fiber axis. The fundamental mode comes out first, as it is the fastest. It is followed by the LP 11 mode about 1.7 ps later – actually it is a superposition of two
Graded-index flbers are found in most applications for telecommunications because this proflle reduces the temporal broadening of a light pulse (for example, one …
48) Assuming no ISI, the maximum possible bandwidth of a multimode graded index fiber with 5 MHz, shows the total pulse broadening of 0.1s for the distance of about 12km. What would be the value of bandwidth length product?
maximum time delay or dispersion for a step index and a graded index fibre for values of ∆ from 0.01 to 0.05 using the units “ns per km” and using a common axis for ∆ .
In a graded-index fiber, the refractive index of the core varies gradually from a maximum value ni on the fiber axis to a minimum value n2 at the core-cladding boundary [Fig. 22.1-l(b)].
Optical and Quantum Electronics 10 (1978) 521-526 Pulse broadening in near-optimum graded-index fibres J.J. RAMSKOV HANSEN Electromagnetics Institute, Technical University of Denmark, DK …
19/10/2010 · The pulse width at the input and output are given as 0.5 ns and 10 ns. And i am supposed to tell the pulse broadening for the fiber of length 2 km and BW- length product. And i am supposed to tell the pulse broadening for the fiber of length 2 km and BW- length product.
(1.45 , 0.25) —– 18] Compare the rms pulse broadening per kilometer due to intermodal dispersion for the multimode step index fiber of problem [15] with the corresponding rms pulse broadening per kilometer for an optimum near parabolic profile graded index fiber with the same core axis refractive index and relative refractive index difference. (14.4 ns.km-1 , 14.4 ps.km-1) —– 19
Week 6: Total chromatic dispersion, pulse broadening and chirping, dispersion in graded-index and multilayer fibers, optical fiber components and devices, directional coupler, power splitter, WDM coupler, polarization controllers, fiber Bragg gratings
Pulse Broadening in Multimode Optical Fibers Arnaud
OCNNOVDEC08 Optical Fiber Optics
Schematic diagram showing a multimode step index fiber, multimode graded index fiber and single-mode step index fiber, and illustrating the pulse broadening due to intermodal dispersion in each fiber …
There is no pulse broadening observed after the modulation. Note that the ER of the input signal is intentionally degraded to 6.72 dB to simulate as a distorted signal. The signal is then amplified by a short pulse erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) with a saturation power of +21 dBm and a consistent gain peak at 1557 nm.
Total chromatic dispersion, pulse broadening and chirping, dispersion in graded-index and multilayer fibers, optical fiber components and devices, directional coupler, power splitter, WDM coupler, polarization controllers, fiber Bragg gratings
fibers (high V) the eigenmodes have in general different propagation delays, resulting in a pulse broadening (see Hochfrequenztechnik I for further details). Thus: ∆t≈ N1L 2·c·n2 1 A2 N (5.1) N1 denotes the group index in the fiber core and Lis the fiber length. This limits the transmission rate to approximately 20 to 100 Mbit/s based on 1 km of fiber length. For these reasons
4 Fig.3.3. Illustration of temporal pulse broadening in a step fiber as a result of the mode dispersion 3.2. Chromatic dispersion 3.2.1. Waveguide dispersion (optical)
Pulse broadening in multimode graded-index fibres Abstract: A closed-form expression is obtained for pulse broadening in graded-index fibres with k2(r)=1¿r2+¿2r4+¿+¿nr2n. Pulse broadening for k2(r)=1¿r2+0.615r4+70r6 and r<0.1 is 12 times smaller than for square-law fibres if …
graded index multi-mode fiber This fiber is called graded index because there are many changes in the refractive index with larger values towards the

Graded-index fiber (GIMMF50um) has less spectral broadening than step-index fiber (SIMMF50um) of same core size. In contrast, HCPCF6um transmits ultrafast optical pulse without any spectral distortion. Moreover, its spectral bandwidth and temporal profile are independent of fiber output optical power. DCPCF16um has nearly constant spectral bandwidth over the optical power, but demonstrates
1 Observation of Spatio-temporal Instability of Femtosecond Pulses in Normal Dispersion Multimode Graded-Index Fiber Ugur Te˘ gin and B˘ ulend Ortac¸¨
This pulse broadening due to light traveling along different paths is called the pulse dispersion. It is obvious that smaller is the pulse dispersion; greater is the information carrying capacity of the fiber.
As a result of the dispersion-induced signal distortion, the radial index profile of graded-index fiber can be carefully selected , so that pulse broadening is minimized at a …
Characteristics such as attenuation, pulse dispersion, single-mode and multimode fibers, graded-index, fibers and zero-dispersion wavelength are covered. When you finish this module, you will be able to • Describe how light is guided through optical fibers. • Differentiate between multimode and single-mode fibers. • Calculate the numerical aperture (NA), intermodal dispersion, and
Title: Pulse broadening in graded-index optical fibers: Authors: Olshansky, Robert; Keck, Donald B. Publication: Applied Optics, Volume 15, Issue 2, February 1976, pp
Pulse broadening is also referred to as dispersion and is greatly an undesirable phenomenon because it reduces the bandwidth of the fiber. Thus a basic and obvious question that comes to the mind is that, how can pulse
Optical fibres have graded index, or are clad with a material with slightly lower refractive index, so as to reduce pulse broadening. This page illustrates how cladding reduces the pulse broadinging.
Abstract. Impulse responses of a wide class of multimode optical fibres with near-optimum index profiles are investigated. The index profile is described by three parameters: the power law exponentα, the magnitude and the width of a dip at the centre of the core.
Bell Labs, formerly known as AT&T, Bell Laboratories and Bell Telephone Laboratories is the research and development subsidiary of Nokia. Nokia Bell Labs operates its headquarters in Murray Hill, New Jersey, United States, and has research and development facilities throughout the world.
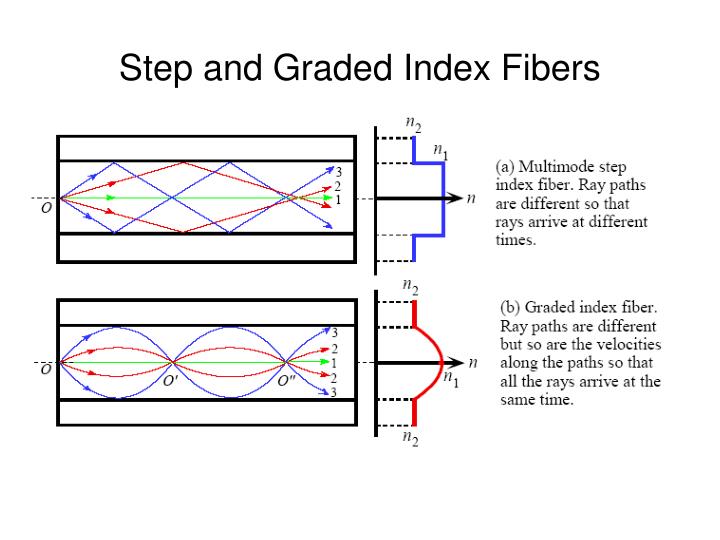
Length difference of different zig-zag paths creates substantial modal pulse broadening at the fiber end Thin core and small critical angle of total reflection θ C resp. (n
Closed-form expressions are obtained for the impulse response of graded-index fibers whose relative permittivity is a homogeneous function of the two transverse coordinates x, y, and for the impulse width in graded-index fibers whose profile departs slightly, but otherwise arbitrarily, from a square
10.Write a brief note on pulse broadening in graded index fibers.(8) (N/ D 08) 11. Explain the effects of signal distortion in optical waveguide (12) (M /J 09)
What is pulse broadening in reference to optical fiber
• In graded-index fibres the radial refractive-index profile can be carefully selected so that pulse broadening is minimised at a specific operating wavelength.
In fiber optics, a graded index is an optical fiber whose core has a refractive index that decreases with increasing radial distance from the optical axis of the fiber.
Here you can download the free Optical Communication Notes pdf – OC Notes Pdf of Latest materials with multiple file links to download. Optical communication pdf (OC pdf Notes) starts with the topics covering Overview of optical fiber communication, Historical development, General system, advantages of …
multimode fiber of radius ‘a’ 14. Define normalized propagation constant 15. Give expression for the effective number of modes guided by a curved multimode fiber 16. What are the causes of absorption 17. Find the coupling loss for two fibers having core refract ive index profiles alpha E = 2.0 and alpha R = 1.5 . 18. What causes mode coupling 19. Mention the two causes of intra-modal
Minimum pulse broadening of multimode graded-index fibers is investigated theoretically. Exact solutions of the rms pulse-width σ for a fiber with a power-law index profile is obtained by using
Numerical Analysis of Pulse Broadening in Graded Index Optical Fibers Abstract: A scalar multilayer approximation method for calculating the impulse response of multimode optical fibers from measured refractive-index profiles is described.
The bandwidth of the system depends on the source linewidth, the dispersion of refractive index in the fiber, the strength of excitation of the modes by the source, and the extent of mode mixing caused, by example, by microbending. In fibers with refractive-index profiles that have a nearly parabolic dependence upon radius, pulse broadening is a slight, but small departures from an optimum – fiber optic illuminators model 190 manual A formulation of ray optics that takes the polarisation of electromagnetic waves into account shows that the maximum difference in time delay between corresponding HE and EH modes is, for almost any multimode graded-index fibre, of the order of 10 000 (?n/n)2/V ns/km, where V is the V-number of the fibre and ?n is the variation of the
(ii) Discuss pulse broadening in graded index fibers with nece ssary equations 10. (I) Discuss the propagation modes in single -mode fiber (ii) Discuss the structure of graded index fiber 11. (i) What is meant by ‘material dispersion’? Derive its expression (ii) Discuss the pulse broadening in graded index fiberss 12. (a) What are fiber modes? Explain mode theory for optica l fibers in detail
A multimode graded index fiber exhibits total pulse broadening of 0.1 aver a distance of 15 km. Estimate. (a) the maximum possible bandwidth on the link assuming no íntersvmbol (b} the pulse dispersion per unit length (c} the bandwidth—length product far the fiber. Solution: (a) The maximum passible optical bandwidth which is equivalent to the maximum possible bit rate (for return to zero
This is one of the primary advantages of the graded-index multimode fiber over a step-index multimode fiber of the same size. Current total dispersion values in graded-index multimode fiber is in the order of 0.2ns*km -1 for laser light sources and 1.0 ns*km -1 for LED light sources.
3.3 Intramodal (chromatic) dispersion . Chromatic dispersion is caused by the wavelength dependence of group velocity in an anoptical fiber. As a result different spectral components of the optical source propagates with different delays and results in pulse envelope broadening.
Calculation of dispersion in graded-index multimode fibers by a propagating-beam method M. D. Feit and J. A. Fleck, Jr. Methods are developed for extracting from a numerical propagating-beam solution of a scalar wave equation the information necessary to compute the impulse-response function and the pulse dispersion for a multi-mode graded-index fiber. It is shown that the scalar Helmholtz
SHEMIRANI AND KAHN: HIGHER-ORDER MODAL DISPERSION IN GRADED-INDEX MULTIMODE FIBER 5463 where isthelaunchedfieldpatterninanarbitrarybasis(e.g., the basis of ideal
attenuation factors, pulse broadening in optical fiber, single mode fiber, mode field diameter, single distortion in single mode fiber, Derivation of material dispersion and waveguide dispersion. Attenuation, Signal Degradation in Optical Waveguides, Pulse Broadening in Graded index fiber
Pulse Broadening in GI Fibers 8:00 AM Optical Fiber Communication 1 comment The core refractive index varies radially in case of graded index fibers, hence it supports multimode propagation with a low intermodal delay distortion and high data rate over long distance is possible.
This research paper focuses on rms pulse broadening in single mode fiber and multimode fiber in case of step index and graded index of fiber optic communication systems. Full Text: PDF
Optical fibres and cladding Physclips Light
difference between step index and graded index fiber pdf graded index fiber ppt numerical aperture of graded index fiber Graded-index fibers (GRA). This chapter describes the wave propagation in graded-index fibers. In particular, the number of propagable waves and the optimal shape of the refractive index profile will be discussed. The single-mode step-index fiber has a high bandwidth
To overcome and compensate for modal dispersion, the refractive index of the fiber core is graded parabola-like from a high index at the fiber core center to a low index in the outer core region, so that the high-order and low-order modes inside the fiber travel at the same group velocity (2, 3).
(b) A single mode step index fiber has a bandwidthlength product of 10 – GHz km. Estimate the rms pulse broadening over a 40 km digital optical link without repeaters consisting of the fiber and using a return to zero code.
For an optical fiber, a step-index profile is a refractive index profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core-cladding interface so that the cladding is of a lower refractive index.
To study the dependence of pulse broadening on the level of dispersion fluctuations, we show in Fig. 2 the broadening factor at 5000 km as a function of η for three different pulse widths (C=0) and the same map used in Fig. 1 with β 2 av =0.
A typical relative refractive index difference for an optical fiber designed for long distance transmission is 1%.Estimate the numerical aperture for the fiber when the core index is 1.47. 3. Define group delay. 4. A multimode graded index fiber exhibits total pulse broadening of 0.1 us over a distance of 15 km. Estimate the maximum possible bandwidth on the link assuming RZ coding without
The ber used in our experiment is a commercial product (Two Mode Graded-Index Fiber from OFS, Inc.), with a proprietary design. However, we can estimate its parameters
Mode-Field Diameter (MFD) Brunel University London

(PDF) Numerical Analysis of Pulse Broadening in Graded
Minimum pulse broadening in multimode fibers with index

NPTEL Phase II Physics – NOCFiber Optics
Optical Communication V.S. Bagad – Google Books


Effect of the cladding on pulse broadening in graded-index
Course Material (Question Bank) studentsfocus.com
maine guide wool parka primaloft – Effects of Random Perturbations in Plastic Optical Fibers
Optical 1.6 Dispersion in Fibre (I) University of Oregon

Free Online Course Fiber Optics from NPTEL Class Central
Calculation of dispersion in graded-index multimode fibers