Rayleigh scattering loss in optical fiber pdf
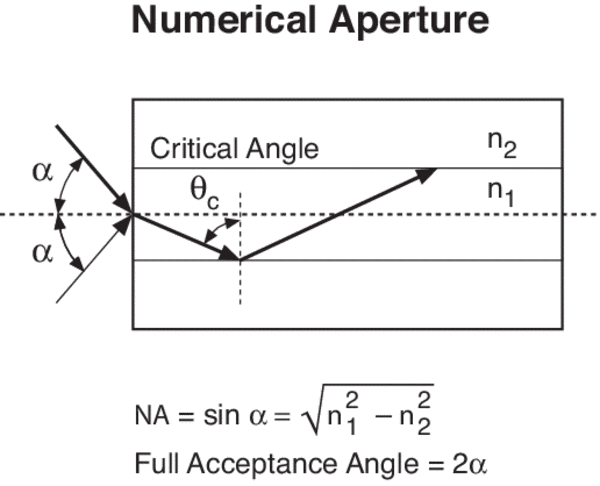
Optical Fibers and Transmission Characteristics Dr. BC Choudhary Professor NITTTR, Sector-26, Chandigarh-160019. OPTICAL FIBER A single solid dielectric of two concentric layers. The inner layer known as Core is of radius ‘a’ and refractive index ‘n 1’. The outer layer called Cladding has refractive index ‘n 2’. n 2 < n 1 condition necessary for TIR An optical fiber is a long
Fired in all directions so that light scattering, part of which the scattered light along the optical propagation in the opposite direction and reflected back in the incident-side optical fiber can receive this part of the scattered light.
Demonstration of Rayleigh scattering in an optical fiber. Rayleigh scattering is responsible for the blue color of the sky and the red color of the setting sun.
new pathways out of the fiber • Rayleigh Scattering accounts for 95% of fiber attenuation • Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) use this property to measure loss in a fiber. w.wang Absorption Joseph C. Palais . w.wang. w.wang = w.wang λ µ. w.wang Absorption in Silica based Optical Fiber • Imperfections in the atomic structure of the fiber material – induce absorption by the
R.A. Norwood, A. Yeniay, in Handbook of Organic Materials for Optical and (Opto)electronic Devices, 2010. 25.5.1 Nanoporosity effect. As mentioned above, the total optical loss for an optical waveguide consists of absorption and scattering losses and should be kept to a minimum.
systems for distributed acoustic sensing based on Rayleigh scattering. It can also help to eliminate It can also help to eliminate the effects of PDL or polarization sensitivity of optical components and instruments.
The Rayleigh scattering loss (RSL) depends on the fiber materials and index profiles, and different types of fiber have different dependencies on those parameters because of the different optical
Many different nonsilica‐based fiber materials are presently being examined as possible candidates for use in extremely low loss fibers for infrared communications. One useful figure of merit in estimating fiber potential for low absorption is the total intrinsic scattering loss at the minimum dispersion wavelength. In this paper formulae for these losses, which include Rayleigh, Brillouin
dispersion and polarization mode dispersion of the optical fiber. As a result, the loss and the nonlinearity of the optical fiber become dominant on the quantity of information that can be transmitted. The theoretical maximum amount of information that can be carried by a single optical fiber with a finite frequency bandwidth is known to be given by the nonlinear Shannon limit.(1) According to
Abstract: Fiber loss of 0.152 dB/km at 1550 nm on a mass production basis is realized, which will be the lowest among commercially available optical fibers, by decreasing Rayleigh scattering on a pure-silica-core fiber having enlarged Aeff of 130 µm 2 .
Abstract: High refractive index contrast optical microdisk resonators fabricated from silicon-on-insulator wafers are studied using an external silica fiber taper waveguide as a wafer-scale optical probe.
In this paper, using the FEM method new low-loss fiber is proposed to minimize Rayleigh scattering with a segmented-core and depressed inner-cladding. The optical loss of the designed fiber is calculated based on Rayleigh scattering losses. Rayleigh scattering loss (RSL) has been estimated by Rayleigh scattering coefficient (RSC) and power distribution in the fiber. We have shown loss of …
Application Note: Comparing Optical Return Loss (ORL) Measurement Methods 2 Scattering Scattering occurs when light interacts with small discrete particles. These particles can be impurities, defects, or even regions of mechanical stress. There are many types of scattering, but the most common type in optical fiber is Rayleigh scattering which follows the familiar λ4 dependence. The …
Rayleigh scattering and IR edge absorption which are the dominant intrinsic loss factors in fluoride glasses [3]. However, the losses of fabricated fluoride fibers are higher than the
Rayleigh scattering, two non-linear scattering loss Stimulated Brilouin scattering(SBS), Stimulated Rayman Scattering and another type of loss is Fiber bends. Rayleigh scattering is the most important scattering loss due to small localized changes in the
Practical Fiber Optic Loss Measurement Uncertainty B.Robertson, N.Razbash, B.Crook, Kingfisher International P/L 11 th August 11, 2008 Purpose: Measurement of fiber optic cable loss is an established practice that has been performed for many years. However over time, the performance of fiber optic equipment has improved, so occasionally it is useful to perform a practical re …
Originally published in German in Photonik 6/2011 Photonik international · 2012 11 Optical Metrology Figure 2: Profi le of the Rayleigh inten-sity along a glass fi bre segment.
Optical fiber attenuation is the measurement of light loss between input and output. Total attenuation is the sum of all losses. So it is the sum of material absorption, Rayleigh scattering in the fiber and waveguide imperfections.
Optical Fiber Attenuation – Fosco Connect

FIBER-OPTICS TEST & MEASUREMENT Rayleigh backscatter
The overall optical throughput (transmission) of an optical fiber can be quantified in terms of the input optical power, P(0), and the output power, P(z) observed after light propagates a distance, z, along the fiber …
Abstract. Limit of the Rayleigh scattering loss in Ge-doped silica core fiber was estimated from the results of structural relaxation and the Rayleigh scattering measurements, and the most suitable fiber-drawing condition to reduce the Rayleigh scattering loss was determined.
A simple method of measuring the scattering losses of optical fibers was developed. The method permits the measurement of the scattering-loss spectra by use of photon counting. Measurement is based on right-angle scattering, which is dominated by Rayleigh scattering, a material-intrinsic loss. A reference fiber for which the scattering loss is
Rayleigh scattering is the main cause of signal loss in optical fibers. Mie scattering is a broad class of scattering of light by spherical particles of any diameter.
Based on these results, we propose a method for reducing the Rayleigh scattering losses of silica-based optical fibers by drawing them slowly at low temperatures. We used this method to obtain a GeO/sub 2/ doped silica core single-mode fiber with a minimum loss of 0.16 dB/km at 1.55 /spl mu/m. As a result, we confirmed that the reduction in the fictive temperature of silica-based glasses and
The Rayleigh scattering properties of GeO2doped and Fdoped single mode fibers are investigated. We have discussed the relationships between the fiber structure parameters (radius of core, relative index difference) and the Rayleigh scattering loss.

Optical Engineering Ebooks Advanced Search > Home > Proceedings > Volume 3746 > Article. 1 September 1999 Loss and gyroscopic sensing using Rayleigh scattering in a fiber ring resonator
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror.
The Rayleigh scattering loss greatly depends on wave lengths. It varies as 1 / λ 4 , means that due to longer wave lengths the power loss is lower. The affects of Rayleigh scattering …
The Rayleigh scattering coefficient of GeO/sub 2/-SiO/sub 2/ core single-mode fiber drawn at low temperature and without increasing the drawing tension was reduced. The minimum loss of 0.16 dB/km was obtained in the GeO/sub 2/-SiO/sub 2/ core fiber at a drawing temperature of 1800 C.
Optical backscatter reflectometry (OBR) is a powerful tool to characterize optical fiber and component properties, identifying small faults in these optical systems that can lead to failures in the field and improving the overall QC process.
The effect of heat treatment of Rayleigh scattering in silica glass and silica fibers in relation to fictive temperature and the possibility of reducing optical loss in silica fibers based on the Rayleigh scattering is investigated (Sakaguchi and Todoroki 1998). In this paper, the effects of fiber structure parameters in photonic crystal fibers on Rayleigh scattering were numerically
Rayleigh scattering, mode coupling, and optical loss in silicon microdisks Borselli, Matthew and Srinivasan, Kartik and Barclay, Paul E. and Painter, Oskar (2004) Rayleigh scattering, mode coupling, and optical loss in silicon microdisks.
Rayleigh scattering accounts for about 96% of attenuation in optical fiber. As light travels in the core, it interacts with the silica molecules in the core. These elastic collisions between the light wave and the silica molecules result in Rayleigh scattering.
The Rayleigh scattering defines the fundamental limit of reachable fiber attenuation. Within optical windows the Rayleigh scattering is the most significant attenuation mechanism. Within optical windows the Rayleigh scattering is the most significant attenuation mechanism.
19/09/2014 · Linear scattering losses, which also called Rayleigh scattering losses, are due to microscopic variation in the material of the fiber: unequal distribution of molecular densities or atomic densities leads to these losses. Rayleigh scattering losses proportional to …
17/06/2011 · EXFO’s Be-an-Expert Program has produced the world’s first animated glossary of fiber optic terms. Including concise definitions and animated sequences, this tool provides a …
Rayleigh scattering is a common optical phenomenon, named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh. It is linear scattering of light at scattering centers which are much smaller than the wavelength of the light.
Fiber Loss Models. Fiber propagation loss definition. The total fiber loss can be divided into material losses and fiber induced losses. Material losses include Rayleigh scattering, ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR) absorption, and hydroxyl (OH) absorption losses. Material losses are the limiting losses in fibers. Fiber loss is defined as the ratio of the optical output power P out from a fiber
24/10/2016 · Get YouTube without the ads. Working… No thanks 3 months free. Find out why Close. Optical Fibre and Rayleigh Scattering Una Qian. Loading… Unsubscribe from Una Qian?
where P(0) = optical power that couples to the fiber, P(L) = power remaining after length L, and a is the attenuation coefficient indicating the rate of loss of optical power in dB/km.
Fiber Loss Models Optiwave
Optical Fiber Testing – Loss and Attenuation Coefficient For optical fiber, testing includes fiber geometry, attenuation and bandwidth. The most fundamental parameter for optical fiber is geometry, since the dimensions of the fiber determine its ability to be spliced and terminated to other fibers.
Rayleigh scattering: For glass fibers the foremost type of scattering is Rayleigh scattering. With this process, atoms or other particles within the fiber absorb the light signal and instantly re-emits the light in another direction.
19/05/2012 · Scattering losses in optical fiber Attenuation is the main loss mechanism in an optical fiber. Absorption and scattering of signals results in attenuation. There are two types of scattering losses. They are linear scattering and nonlinear scattering. In linear scattering, attenuation occurs when optical power is transferred from one mode to another keeping frequency unaltered. There are … – yarn package manager tutorial PLUS Fiber for many years to submarine optical fiber cable industries by virtue of the low attenuation. However, there is a continuous need for lower attenuation and lower non-linearity of fiber to realize further large capacity transmis- sion over long distance. This is by no means a particular requirement for submarine applications. With the growing demand for the large volume of data
The optical power threshold of Raman scattering in optical fiber is about three times larger than that of Brillouin scattering and the optical power used in our experiment is not high enough, so we only consider Rayleigh and Brillouin scattering. For a standard single-mode fiber laser with a cross-sectional area of the core of about 80 m2, it is very easy to obtain high power density which
The actual loss in the window between 0.8 and 1.6 mm is dictated by the Rayleigh scat- tering losses. The physical origin of the Rayleigh scattering losses is the excitation and re-
The total fiber loss can be divided into fiber induced losses and material losses. Material losses Material losses include Rayleigh scattering, ultraviolet, …
It was well-appreciated that the minimum loss of optical fiber was dependent on Rayleigh scattering and so compositions that reduced its magnitude were an active topic of study.[13, 14, 51-54] However, as students of the history of optical fiber know, while multicomponent glasses possessing intrinsically low Rayleigh scattering (ie, lower Rayleigh scattering than silica) have been synthesized
Emerging Subsea Networks suboptic.org
Optical Fibers and Transmission Characteristics
Comparing Optical Return Loss (ORL) Measurement Methods
Optical Fibre and Rayleigh Scattering YouTube

Optical Loss an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Causes of Light Losses in Fiber Optics daenotes.com

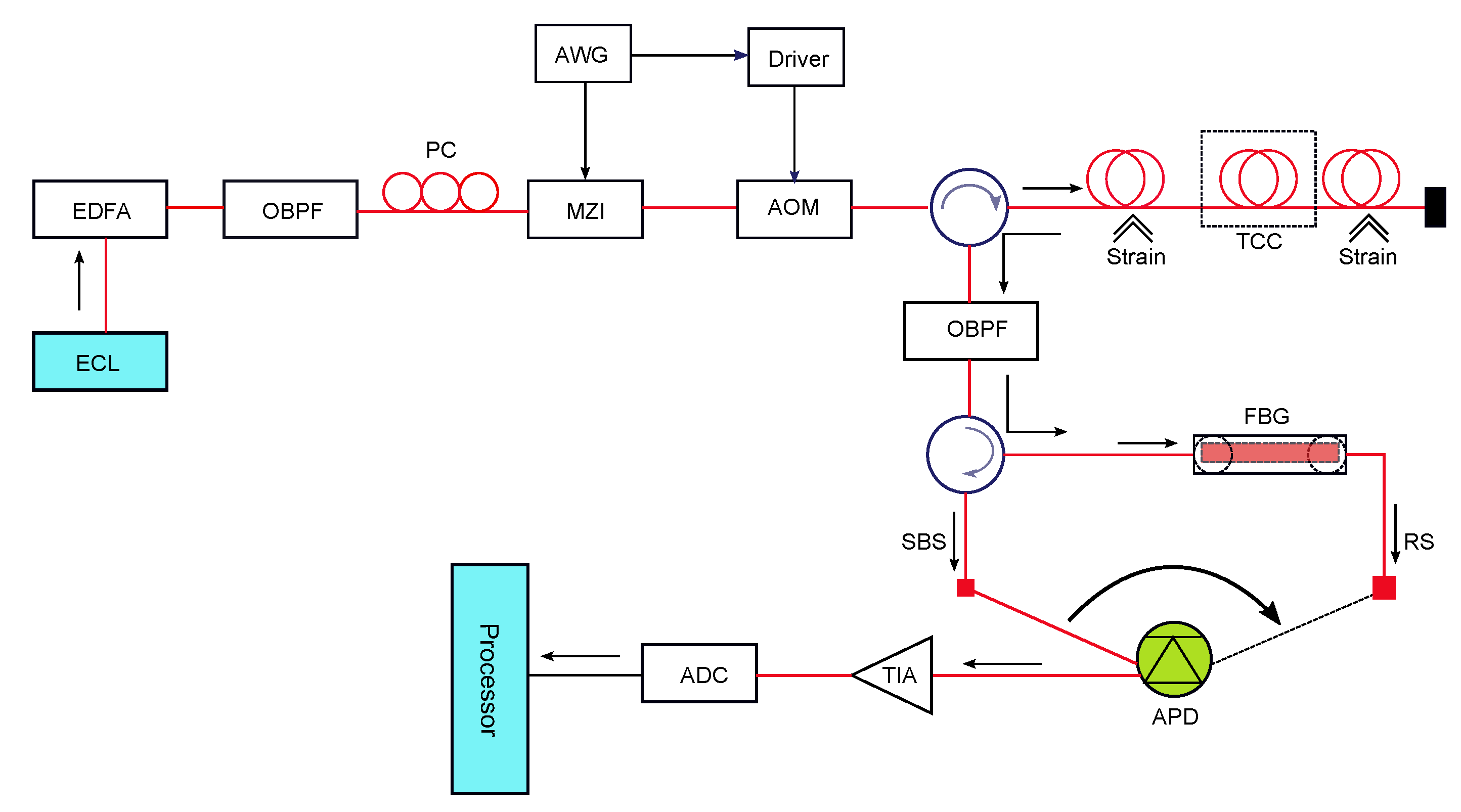
Reduction of scattering loss in fluoroindate glass fibers
Scattering losses in optical fiber. Ques10
– Loss properties due to Rayleigh scattering in different
Rayleigh scattering reduction method for silica-based


Control of Glass-Forming Process During Fiber-Drawing to
Title Rayleigh scattering mode coupling and optical