Modes of propagation in optical fiber pdf
Robust Location of Optical Fiber Modes via the Argument Principle Method Parry Y. Chen1,2 and Yonatan Sivan2 1School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Israel
develop optical fiber communication systems and planar lightwave circuits thor- ough understanding of the principle of lightwave propagation and its application to the design of practical optical …
Modes of Propagation Though optical fiber should support any numbers of rays for propagation practically it is found that it allow only certain restricted number of rays for propagation. The maximum number of rays supported by the fiber is called Modes of propagastion.
In conclusion, we analyze the mode properties and propagation effects of OAM modes in the ring fiber and propose to use the optical OAM modes in a multiple-ring fiber for space- and mode- …
multimode fiber is derived from the fact that the core of the fiber will support hundreds of different optical paths for the light to traverse from one end of the fiber to the other, each with its own propagation time.
Abstract— Multimode fibers are characterized by multipath propagation of optical signals which leads to severe Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) at the output of the fiber.
Photonics Communications Engineering, OPTI 500B, Lectures 17 and 18 11/17 Linearly Polarized (LP) Optical Fiber Modes . It is customary in the theory of optical fibers to make the
Dispersion in an optical fiber is the “spreading” or broadening of a light pulse during its propagation along the fiber. There are two main types of light dispersion in optical fibers: chromatic, which deals with the light spectral properties, and modal, which deals with the path (i.e., mode) of each light ray inside the fiber.
Module 2 – Linear Fiber Propagation . Dr. E. M. Wright Professor, College of Optics, University of Arizona . Dr. E. M. Wright is a Professor of Optical Sciences and Physic sin the University of Arizona. Research activity within Dr. Wright’s group is centered on the theory and simulation of propagation in nonlinear optical media including optical fibers, integrated optics, and bulk media
Lecture 5: Optical fibers These modes result from skew ray propagation (helical path without passing through the fiber axis). The modes are denoted as HE lm and EH lm depending on whether the components of H or E make the larger contribution to the transverse field. core cladding • The full set of circular optical fiber modes therefore comprises: TE, TM (meridional rays), HE and EH (skew
form along the axis of propagation (an ideal fiber) or may be nonuniform (a nonideal fiber). Suppose that a normalized electric field pattern ja with an amplitude e a at the fiber input propagates to a field pattern jb with an amplitude e b at the output. We represent this propagation by e bjb Te aja, (1) where T v is an N 3 N matrix representing propa-gation (both loss and phase change), as
Fiber-optic systems are used in most modern telemedicine devices for transmission of digital diagnostic images. Other applications for optical fiber include space, military, automotive, and the industrial sector.
Fig. 1 Schematic of the step-index fiber and its modes; (a) structure of the fiber composed of a protective coating, cladding and core where the light is guided; schematic of the mode patterns and spectrum for (b) the scalar approximation and (c) the natural vector modes with partialy resolved degeneracy of the first higher order mode group.
For light propagation through the fiber, the conditions for total internal reflection (TIR) should be met at the core-cladding interface Light Propagation through Optical Fiber
If the fiber losses are only 0.2 dB/km, this means that even after 100 km of propagation distance one still has 1% of the original optical power. That is often sufficient for reliable detection of data signals, even at very high bit rates.
Analysis Of Linearly Polarized Modes . Author Ioana Moldovean mode of step index fiber optic. Currently, the propagation beam method is widely used to study the propagation of light. There are three version of beam propagation method (BPM). The first BMP is based on the fast Fourier transform, the second is based on finite difference method and the third is based on the finite element
Modes of Propagation in an Optical Fibre Physics Forums

Propagation Modes Optical Fiber edaboard.com
This articles discusses propagation modes of light in free space, in a transparent homogeneous medium, in a waveguide structure, or in an optical resonator. Alternatively, the term “mode” can also mean a mode operation], e.g. continuous-wave mode locking, Q switching, or single-frequency operation; for such information, see the article on modes of laser operation. When some light beam
hybrid mode is in fact the lowest order mode that can propagate in an optical fiber. Since hybrid mode is the lowest order mode, it can be analytically shown that the mode of the ray that propagates in the fiber along the axis is hybrid in nature.
optical fiber, one should consider a limitation imposed on the propagation by the boundary conditions of the fiber as well as the refraction index of the core and the cladding described by so- 7

14/05/2018 · What actually is a mode of optical fiber propagation?Is it similar to modes which correspond to various configurations as in standing waves on a string ? Also How correct is it to consider no. of rays as no of modes? Officially, a fiber mode is a subset of ‘waveguide modes…
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University . The Nature of Light • Quantum Theory – Light consists of small particles (photons) • Wave Theory – Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave • Ray Theory – Light travels along a straight line and obeys laws of geometrical optics. Ray theory is valid when the objects are much larger than the
Single-mode optical fiber is an optical fiber in which only the lowest order bound mode can propagate at the wavelength of interest typically 1300 to 1320nm. jump to single mode fiber page Multi-Mode cable has a little bit bigger diameter, with a common diameters in the 50-to-100 micron range for the light carry component (in the US the most common size is 62.5um).
• Discuss light propagation in an optical fiber • Identify the various types of optical fibers • Determine the dispersion characteristics for the various types of optical fibersDescribe the various connector types • Calculate decibel and dBm power • Calculate the power budget for a fiber optic system • Calculate the bandwidth of a fiber optic system • Describe the operation and
OPTICAL FIBERS AND FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS10 .5 FIGURE 2 Ray path in a gradient-index fiber . number of modes must be characterized by solving Maxwell’s equations with the appropriate boundary conditions for the structure. Fibers which exhibit a discontinuity in the index of refraction at the boundary between the core and cladding are termed step-index fibers . Those …
Module 3 : Wave Model Lecture 3.1 : Wave Model – I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Analysis of cylindrical waveguides Characteristic Equation (Eigen Value Equation) Modes of optical fiber MODAL PROPAGATION INSIDE AN OPTICAL FIBER (WAVE MODEL-I) 1. Basics 1. There are certain limitations to ray model. 2. The ray model does not predict correctly that even after …

Single Mode Optical Fiber – Nonlinearity 1 as a function of propagation distance. 5 From the theory on dispersion, the chirp parameter is scaled by the pulse width, 0 in the equation: 𝜔= 𝑇0 2𝑡. ( 8 ) 2.3 FUNDAMENTAL SOLITONS As the previous simulations have just shown, SPM chirps the Gaussian pulse with a positive chirp. In fact the relationship is a little more complicated as
In a multimode type fiber, the optical energy is propagating in different modes. Now I my question is that, when some optical energy is launched into such a fiber, how is the energy distributed among all possible propagating modes?
Soliton Propagation in a Single-Mode Optical Fiber An optical soliton forms due to the interplay of anomalous group velocity dispersion (GVD) and self-phase modulation (SPM) in an optical fiber.
Fiber Propagation Modes. Scalar fiber modes. The designation of Linearly Polarized (LP) Fiber modes is based on the assumption of weak guidance. Weakly guiding fibers have a small difference between core and cladding refractive index. Two numbers designate the LP (m, n) modes: m – azimuthal number . n – orbital number where m = 0, 1, 2, … and n = 1, 2… Both guided and cladding modes …
In this study, a wavelength modulation fiber-optic SPR sensor is designed, and theoretical analysis of optical propagation in the optical fiber is also done. Compared with existing methods, both the transmission of a skew ray and the influence of the chromatic dispersion are discussed. The resonance wavelength is calculated at two different cases, in which the chromatic dispersion in the fiber
single mode fiber: multi-mode fiber: graded index MMF: Wave propagation in cylindrical optical waveguides Waveguides for signal transmission must propagate a wave longitudinally in the z-direction (β
Theory of Light Propagation in Optical Fiber 9 Geometrical optics can’t describe rigorously light propagation in fibers 9Must be handled by electromagnetic theory (wave propagation)
Optical fiber communication system is a communication system in which information is transmitting through one place to another by sending pulses of light through optical fiber. …
the optical fiber made of silica glass, is the light transmission area of the fiber. It may sometimes It may sometimes be treated with a “doping” element to change its …
2/06/2011 · Unfortunately, the phrase “only certain angles of propagation can transmit down an optical fibre” is misleading, because when discussing electromagnetic propagation in waveguides it makes more sense to say “certain *modes* can transmit down an optical fibre”- the meaning is different, and modes, a wave concept, is more appropriate for spatially confined light than ray concepts.
Modes of Propagation and Types of Optical Fibers
Theoretical Analysis of the Optical Propagation Characteristics in a Fiber-Optic Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Linlin Liu 1 , Jun Yang 1, *, Zhong Yang 2 , …
The invention relates to an optical fiber as an optical waveguide for the single-mode operation. The present invention proposes a fiber having a microstructure, by which the propagation of modes of a higher order are selectively suppressed in the optical waveguide. At the same time, the propagation of transversal modes of a higher order is
Modes in cylindrical optical fiber are determined by the wave equation(s) in cylindrical coordinates: 2 E z 1 E z 1 2 Ez 2 q Ez 0 2 2 2 r r r r 2 H z 1 H z 1 2H z 2 q Hz 0 2 2 2 r r r r . . The solutions for the core and cladding regions must match at the boundary. and z. φ. The φ and z functions are exponentials of the form ei . the residual wave equation in the r coordinate is of the form
The light propagation, along a waveguide can be described in terms of a set of guided electromagnetic waves, called as modes of the waveguide. Working Principle A fundamental optical parameter one should have an idea about, while studying fiber optics is Refractive index .
Bombay Page 2 INTRODUCTION Fiber-Optic Communication is the most modern and advanced mode of data medium, led to development of optical fiber communication.
The propagation of light energy in optical fiber takes place at different angles of propagation called modes of propagation. Since all rays with the angles less than θ C , propagate in fiber. So on basis of the electromagnetic theory these rays propagate at distinct angles, shown as:
Three types of propagation modes are revealed on the basis of in situ observation and speed measurement of fiber fuse propagation and the damage morphology of fused fibers. The difference comes from the plasma volume confined in the fiber core as summarized in Fig. 2.9 .
propagation determine the efficiency of light propagation in the fiber. A mode is the path that light takes when it travels through a fiber. The different modes are depicted in figure 2. The refractive index profile determines the possible modes that the light rays assume. Step-index fibers may be single or multi-mode fibers. In multi-mode, step-index fibers, light may travel in different
The phase shift plays an important role in light propagation in optical fiber. We will We will use this relation later, discussing mode types and the range of guided modes.
The propagation of higher modes, such as the LP 11 mode, in optical nanofibers using the exponentially tapered optical fiber as a basic model is investigated. – whos afraid of virginia woolf play pdf Wave propagation in opticalfibers Optical fiber Optical fiber consists of a cylindrical core of almost pure silica glass surr…
• Mode scrambler • Arc fusion •What are the techniques to mitigate propagation loss in optical fibers? •In principle, can we create an optical fiber with zero loss? •What does a scientist need to do to win the Nobel prize? •Since optical fiber has such a low propagation loss, could it be a good platform to transfer energy (like the electrical grid) to home? •Fiber optics
Abstrat — This paper addresses thepulse propagation through a fiber optic system, operating in linear and nonlinear regimes. After a brief introduction to optical fibers, we …
Here we employ both dynamic and geometric phase control of light to produce radially modulated vector-vortex modes, the natural modes of optical fibers.
multi-mode fiber (MMF) in which the number of resolvable image features approaches four times the number of spatial modes per polarization propagating in the fiber.
propagation of light along a fiber The concept of light propagation, the transmission of light along an optical fiber, can be described by two theories. According to the …
Fiber-optic cable has two propagation modes: multimode and single mode. They perform differently with respect to both attenuation and time dispersion. The single-mode fiber-optic cable provides much better performance with lower attenuation. To understand the difference between these types, you must understand what is meant by “mode of propagation.”
There are 2 types of propagation mode in fiber optics cable which are multi-mode and single-mode. These provide different performance with respect to both attenuation and time dispersion. The single-mode fiber optic cable provides the better performance at a higher cost.
OPTICAL FIBERS (3 Lab Periods) propagating in an optical fiber. The propagation constant β is shown as a function of V. Each V represents a dif-ferent fiber configuration or a differ-ent light wavelength in a given fiber configuration. For waveguides in which the diameter of the core is extremely large compared to λ, the lowest order mode has an irradiance profile which is Gaussian. That
The last situation leads to an increased distortion of the signal due to the different propagation velocities of the modes. 3.2- Fibre types The refractive index of the core of an optical fibre is generally a function of the core radius r .
Cross section view of optical fiber and single fiber cable Single Mode (SM) vs. Multi-Mode (MM) Fiber There are a few factors that contribute to the type of mode propagation a fiber will demonstrate.
Single Mode Optical Fiber – Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports only a single transverse mode. The benefits of supporting only a single mode is that modal dispersion is eliminated since all pulses travel with the same modal group velocity. The
• Light propagation in optical fibre •From previous equation is possible to derive the maximum entrance angle θ 0,max nsin θ 0,max =n 1sin θ c=(n 1 2-n 2 2)1/2 where θ c = π/2- ϕ c. •Previous equation defines also the Numerical Aperture NA=nsin θ 0,max≅n 1(2∆)1/2 where ∆=(n 1-n 2)/n 1 and last relation is a good approximation if ∆ is much less then 1. NA describes the
Mode Theory . The mode theory, along with the ray theory, is used to describe the propagation of light along an optical fiber. The mode theory is used to describe the properties of light that ray theory is unable to explain.
The invention relates to an optical fiber as an optical waveguide for the single-mode operation. The present invention proposes a fiber having a microstructure, by which the propagation of modes of a higher order are selectively suppressed in the optical waveguide.
Propagation of Light and Modes in Optical Fibers
Pulse Propagation in Optical Fibers ULisboa

(PDF) Fiber propagation of vector modes ResearchGate
Single Mode Optical Fiber Nonlinearity Amazon S3

Analysis on Dispersion & Propagation Optical Fiber of
Improvement of Transmission Propagation of Multimode

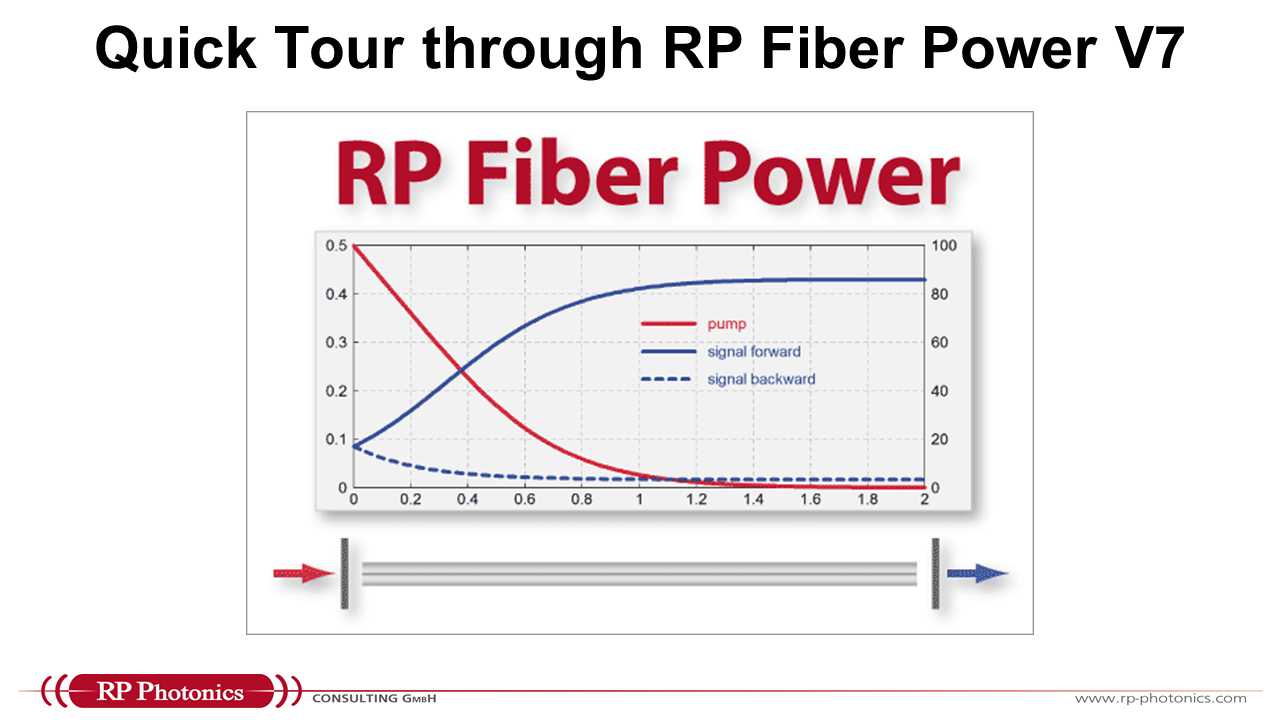
Module 2 – Linear Fiber Propagation
Analysis Of Linearly Polarized Modes comsol.com
– Robust Location of Optical Fiber Modes via the Argument
System. Light propagation in an Optical Fiber. – Mode
Fiber Fuse Propagation Modes SpringerLink
Fiber Propagation Modes Optiwave
Module 2 – Linear Fiber Propagation
1. Soliton Propagation in a Single-Mode Optical Fiber
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University . The Nature of Light • Quantum Theory – Light consists of small particles (photons) • Wave Theory – Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave • Ray Theory – Light travels along a straight line and obeys laws of geometrical optics. Ray theory is valid when the objects are much larger than the
single mode fiber: multi-mode fiber: graded index MMF: Wave propagation in cylindrical optical waveguides Waveguides for signal transmission must propagate a wave longitudinally in the z-direction (β
Fiber-optic cable has two propagation modes: multimode and single mode. They perform differently with respect to both attenuation and time dispersion. The single-mode fiber-optic cable provides much better performance with lower attenuation. To understand the difference between these types, you must understand what is meant by “mode of propagation.”
Analysis Of Linearly Polarized Modes . Author Ioana Moldovean mode of step index fiber optic. Currently, the propagation beam method is widely used to study the propagation of light. There are three version of beam propagation method (BPM). The first BMP is based on the fast Fourier transform, the second is based on finite difference method and the third is based on the finite element
If the fiber losses are only 0.2 dB/km, this means that even after 100 km of propagation distance one still has 1% of the original optical power. That is often sufficient for reliable detection of data signals, even at very high bit rates.
OPTICAL FIBERS (3 Lab Periods) propagating in an optical fiber. The propagation constant β is shown as a function of V. Each V represents a dif-ferent fiber configuration or a differ-ent light wavelength in a given fiber configuration. For waveguides in which the diameter of the core is extremely large compared to λ, the lowest order mode has an irradiance profile which is Gaussian. That
Modes of Propagation Though optical fiber should support any numbers of rays for propagation practically it is found that it allow only certain restricted number of rays for propagation. The maximum number of rays supported by the fiber is called Modes of propagastion.
• Discuss light propagation in an optical fiber • Identify the various types of optical fibers • Determine the dispersion characteristics for the various types of optical fibersDescribe the various connector types • Calculate decibel and dBm power • Calculate the power budget for a fiber optic system • Calculate the bandwidth of a fiber optic system • Describe the operation and
For light propagation through the fiber, the conditions for total internal reflection (TIR) should be met at the core-cladding interface Light Propagation through Optical Fiber
multimode fiber is derived from the fact that the core of the fiber will support hundreds of different optical paths for the light to traverse from one end of the fiber to the other, each with its own propagation time.
Theory of Light Propagation in Optical Fiber 9 Geometrical optics can’t describe rigorously light propagation in fibers 9Must be handled by electromagnetic theory (wave propagation)
optical fiber, one should consider a limitation imposed on the propagation by the boundary conditions of the fiber as well as the refraction index of the core and the cladding described by so- 7
Cross section view of optical fiber and single fiber cable Single Mode (SM) vs. Multi-Mode (MM) Fiber There are a few factors that contribute to the type of mode propagation a fiber will demonstrate.
Theoretical Analysis of the Optical Propagation
Improvement of Transmission Propagation of Multimode