Man made fibres and their properties pdf
Natural fibres including linen and hemp are human friendly in every way. They guarantee high comfort as well as environment protection. Testing of clothes on the human organism is a necessity.
Man-made vitreous fibers (MMVF), also called man-made mineral fibers (MMMF) and synthetic vitreous fibers (SVF), are a group of fibrous, inorganic materials, generally aluminum or calcium silicates, that are derived from rock, clay, slag and glass.
Examples of man made fibres are viscose rayon, acetate rayon, nylon, polyester etc. Depending on raw material chosen for making of the fibres they are classified as cellulosic fibres, protein fibres and
Man-made fibers are fibers in which either the basic chemical units have been formed by chemical synthesis followed by fiber formation or the polymers from natural sources have been dissolved and regenerated after passage through a spinneret to form fibers.
Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres that derived from chemical resources (Achwal 1984). Synthetic fibres are continuous filament form during fibre extrusion process at the stage of manufacturing either dry or wet or melt spinning methods, which means the fibres come in long lengths. Synthetic fibres are manufactured using plant materials and minerals: viscose comes from pine trees or
On the basis of their origin, fibres are classified as Synthetic Fibres. Synthetic fibres are the man-made polymers designed to make a fabric. Polymers are obtained when many small units are joined together chemically. Some of the examples of synthetic fibres are: Rayon: It is made from wood pulp. It is also known as artificial silk as it has characteristics resembling silk. Nylon: It was
Fibers can be divided into natural and man-made (synthetic) substance, their properties can affect their performance in many applications. Nowadays, man-made fiber materials are replacing other conventional materials like glass and wood in a number of applications [10] .
modified during the manufacturing process. Man-made fibres High Performance And High Temperature Resistant Fibers 1 High Performance And High Temperature Resistant Fibers – Emphasis on Protective Clothing I.
Fibres have traditionally been used in all cultures of the world to meet basic requirements of clothing, storage, building material, and for items of daily use such as ropes and fishing nets.
Filaments are related to man-made fibres. The single strand of the continuous filament is called monofilament. Silk is the only natural fibre which belongs to this group. Natural fibre length varies fibre to fibre, lot to lot, but man-made fibre length is controlled by the manufacturer, possible to cut the filament in any length he wishes. Textile Fibre and its Classification: All fibres are
their properties (strength, elasticity, or elastic modulus) [7, 12, 13]. An understanding of the mechanism of the mutual effect of An understanding of the mechanism of the mutual effect of the CF and the polymeric binder on the structure and properties of each other has made it …
Chemistry Articles. Synthetic Fibre. Fibre Synthetic Fibres and their Uses. Synthetic fibre are man-made fibres, most of them are prepared from raw material (petroleum) called petrochemicals. All fabrics are obtained from fibres and fibres are obtained from artificial or man-made sources. It consists of small unit or a polymer which is made from many repeating units known as monomers
Properties of man-made fibre yarns spun on DREF-3 spinning system A R Padmanabhan The South India Textile Research Association. Coimbatore 641 014. India Received 16 April 1991: accepted 29 May 1991 To explore the potentialities of the DREF-3 friction spinning system for processing man-made fibres. 6s and 12syarns were produced from 100% polyester. 100% viscose. polyester/cotton and …
ing, and textile science need not only a listing of fibers and fiber properties but also a firm foundation in the relationship of fiber structure to the physical and chemical properties of fibers, as well as the consumer end-use properties that
Students are encouraged to examine the fabric their clothes are made from and make connections between the properties of the fabrics and their uses. The properties of Linen and Lycra are compared
Man-made Fibres • Textile Fibre Parameters • fibres and their properties. Textile fibres are used for a wide range of applications such as covering, warmth, personal adornment and even to display personal wealth. Textile technology has come a long way in meeting these requirements. A basic knowledge of textile fibres will facilitate an intelligent appraisal of fibre brands and
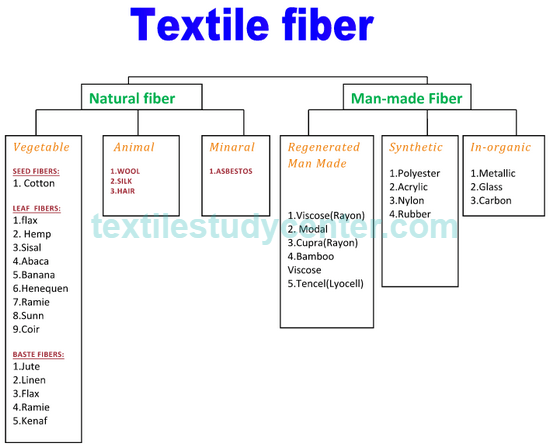
The Classification of man-made fibers Man-made fibers are classified into three classes, those made from natural polymers, those made from synthetic polymers and those made from inorganic materials.
This Indian Standard was adopted by the Bureau ofIndian Standards. after the draft finalized by the Man Made Fibres, Cotton and Their Products Sectional Committee had been approved by the Textile Division Council. Textiles. in recent years. have become fashion oriented and their constructional details vary with the taste of customer. appeal. serviceability, aesthetics. durability and end use
contains information on the whole spectrum of man-made fibers (including raw materials, basic fiber technology, fiber properties, end- uses, global statistics), and includes new fiber developments
Respiratory health effects of man-made vitreous (mineral

Classification of Fibers. Rayon Fibers
Man-made fibres are divided into two categories regenerated and synthetic fibres. Textile fabrics are produced by interlacing or entangling yarns or fibres in
Textile Fiber Parameters Fibrous materials should possess certain properties for them to be usekl as textile raw materials. Those properties which are essential
High performance fibres, and more specifically aramids for their outstanding heat and mechanical properties, although most often used as reinforcing compound, are also used more uniquely and directly in situations where

6/03/2012 · A sound basic knowledge of fibres and fabrics is essential for success. Students need to understand how the combined properties of the fibres and the fabric construction make fabrics appropriate for their intended use. Fibres Fibres are the basic building blocks of fabrics. Fibres must be twisted (spun) together to make a yarn before they can be made into a fabric. Fibres are either man-made
If it is desired to produce composites with high mechanical properties the short fibres need to be replaced by continuous forms such as roving, yarn and fabrics to
Jai Shri Ram 3 and natural fibres with varying linear density to provide an optimum performance. The heavy weight fabrics for outerwear are multi-layered (coated or laminated) and their properties differ
Synthetic mineral fibres (SMF) is a generic term used to collectively describe a number of amorphous (non-crystalline) fibrous materials including glassfibre, mineral wool and ceramic fibre. Much of the international literature refers to SMF as ‘Man Made Mineral Fibres’ (MMMF). Glassfibre and mineral wool have been used for many decades. The major application of SMF materials is in thermal and
• Comparisons of the properties of natural and man-made materials, revealing their comparative efficiencies • Substitution studies exploring the potential for one to substitute for another, suggesting where man-
origin of different fibres is investigated and students learn about the properties of natural and man- made fabric and what a material suitable for it’s use. Students need to develop a clothing label
problems relating to the quality of products processed from man-made fibres, the use of the new types of viscose rayon staple fibres (high-modulus and polynosic) with their good hygienic
Man-made fibres are fibres in which either the basic chemical units have been formed by chemical synthesis followed by fibre formation or the polymers from natural sources have been dissolved and regenerated after passage through a spinneret to form fibres.
The reader will learn what man-made mineral fibres are, which factors determine their risks to human health and information of the putative and established substitutions of carcinogenic fibres. For more details on the group of fibres known as man-made vitreous fibres (MMVF) the WHO publication on this topic provides extensive information [1] .
Get this from a library! Manual of man-made fibres; their manufacture, properties, and identification.. [C Z Carroll-Porczynski]

physiomechanical properties and application of man.made fibres biologically active collagen fibres and fibrous materials m. p. vasil’ev and l. a. vol’f udc 677.472.6
Classification of Fibers. – Download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online. Classification of man-made fibres and their codes.
The Properties of Man-made Fibres The technical advantages The advantages for the consumer Designation of Man-made Fibres Titre designations Heat-Setting The process The advantages Apparel Manufactured from Man-made Fibres The fabrics The system The functions The Care Properties Handling of textiles The care symbols for textiles The properties of textiles The Significance of Man-made Fibres
Natural fibres with their long history of serving mankind are very important in a wide range of applications, and they compete and co-exist in the twenty-first century with man-made fibres, especially as far as quality, sustainability and economy of production are concerned. This ‘Introduction’ describes the classification of natural fibres, levels of production and advantages derived from
Man-made fibre, fibre whose chemical composition, structure, and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process. Man-made fibres are spun and woven into a huge number of consumer and industrial products, including garments such as shirts, scarves, and hosiery; home
natural fibres and man-made or chemical fibres. Flax is considered to be the oldest and the most used natural fibre since ancient times 2 “fiber” or “textile fiber” A unit of matter which is capable of being spun into a yarn or made into a fabric by bonding or by interlacing in a variety of methods including weaving, knitting, braiding, felting, twisting, or webbing, and which is the
MAN-MADE VITREOUS FIBERS med.navy.mil
change in properties of man-made fibres and fabrics made from them under the action of epoxy resins k. e. perepelkln and n. p. alekseenko udc 677.017.427:677.017.63
ABSTRACT: The group of man-made mineral or vitreous fibres (MMMFs or MMVFs) includes glass wool, rock wool, slag wool, glass filaments and microfibres, and refractory ceramic fibres (RCFs).
are known as man-made fibres and these are of following two types: a) Regenerated fibr es – These fibres are made from extremely small cotton fibres or any other fibre …
Man-made fibres have already begun to dominate the market. Cotton has always been a big seller, and their performance properties are not so good. The problem is that the melting point of the polymer is lower and this sets limitations on its production and its applications. For example, ironing temperatures are limited.’ There are drawbacks, agrees Fletcher. ‘But, what’s critical is – virginia woolf mrs dalloway pdf francais MAN-MADE MINERAL FIBRES 41 ‘S’ glass is a high-strength glass developed in about 1960 for applications such as rocket motor cases. Produced only in the USA, it …
The main goal of this work was to study the Influence of sportswear fabric properties on the physiological responses and performance of athletes.
The fabrics made of synthetic fibres like polyester and nylon are easily heat-set, i.e., they retain the fold or pleat made on them by ironing even after washing. Thus it is easier to maintain clothes made of synthetic fibres than those made of natural fibres.
These four account for approximately 98 percent by volume of synthetic fiber production, with polyester alone accounting for around 60 per cent. [11] There are several methods of manufacturing synthetic fibers but the most common is the Melt-Spinning Process .
However, man-made fibres are lack of natural structure such as resiliency and good appearance of the woven carpets. Heat setting plays a very important role in producing filament yarns with desired properties.
from each other and man-made fibres can be confused with the natural fibre they are imitating, such as rayon for silk. Using simple microscope can enable you to identify many natural fibres.
properties, with reference to their uses and application in Cape Verde fisheries. Dyneema is the newest of these fibres and will be given special attention in this study. 1.1 Cape Verde Islands and their …
Natural and Man-Made Fibers and their Role in Creation of Physiological State of Human Body Citations Metrics; Reprints & Permissions; PDF Abstract. Natural fibres including linen and hemp are human friendly in every way. They guarantee high comfort as well as environment protection. Testing of clothes on the human organism is a necessity. New and more sophisticated technologies are being
properties and offer significant reduction in the cost and also associated benefits with processing in comparison to synthetic fibre [9, 10]. This study is an attempt to study the effect of both synthetic and natural fibres
They have different physical and chemical properties and they are different in chemical composition. Difference Between Natural Fiber And Synthetic Fiber: Difference between natural and synthetic fibers is given below. Natural Fiber Synthetic Fiber ; 1.All of the natural fiber comes from nature. 1.Synthetic fibers are completely man made. 2.Length of the fiber is nature given. 2.Length of the
Man-Made Fibres As the name itself indicates these textile fibres are made by man to meet the particular requirements. The chemical composition, structure, and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process.
stretched satisfactorily without significant deterioration in their tensile properties, ifhot 8%solution of sodium chloride isused as the rinsing medium to remove the alkali. Slack mercerization reduces tenacity and increases breaking elongation; however, stretching after mercerization increases the tenacity and lowers the breaking elongation ofcotton-man-made fibre blends. Pure cotton yarns
This report analyzes the worldwide markets for Cellulosic Man-Made Fibers in Thousand tons. In addition, the Global and the US markets are analyzed by the following Applications: Clothing, Spun Yarn, Fabrics, and Other Applications.
Natural and Man-Made Fibers and their Role in Creation of
Classification of man-made fibers and their codes
High performance fibres and the mechanical attributes of
Effect of Heat Setting Process for Polymers Formatex

Hygienic and comfort qualities of man-made fibres and
The Way From Production To Use Marmara Üniversitesi
INFLUENCE OF KENAF AND POLYPROPYLENE FIBRES ON
Linen Fibres Based Reinforcements for Laminated Composites
– Man Made Fibre Process TEXTILE LIBRARY
BBC Northern Ireland – For Teachers – KS2 Linen Thematic


CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRES Govt.college for girls sector
PHYSIOMECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF MAN.MADE FIBRES
Man-made /Artificial fibers Textile School
CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRES Govt.college for girls sector
Properties of man-made fibre yarns spun on DREF-3 spinning system A R Padmanabhan The South India Textile Research Association. Coimbatore 641 014. India Received 16 April 1991: accepted 29 May 1991 To explore the potentialities of the DREF-3 friction spinning system for processing man-made fibres. 6s and 12syarns were produced from 100% polyester. 100% viscose. polyester/cotton and …
Natural fibres with their long history of serving mankind are very important in a wide range of applications, and they compete and co-exist in the twenty-first century with man-made fibres, especially as far as quality, sustainability and economy of production are concerned. This ‘Introduction’ describes the classification of natural fibres, levels of production and advantages derived from
Synthetic mineral fibres (SMF) is a generic term used to collectively describe a number of amorphous (non-crystalline) fibrous materials including glassfibre, mineral wool and ceramic fibre. Much of the international literature refers to SMF as ‘Man Made Mineral Fibres’ (MMMF). Glassfibre and mineral wool have been used for many decades. The major application of SMF materials is in thermal and
Examples of man made fibres are viscose rayon, acetate rayon, nylon, polyester etc. Depending on raw material chosen for making of the fibres they are classified as cellulosic fibres, protein fibres and
High performance fibres, and more specifically aramids for their outstanding heat and mechanical properties, although most often used as reinforcing compound, are also used more uniquely and directly in situations where
stretched satisfactorily without significant deterioration in their tensile properties, ifhot 8%solution of sodium chloride isused as the rinsing medium to remove the alkali. Slack mercerization reduces tenacity and increases breaking elongation; however, stretching after mercerization increases the tenacity and lowers the breaking elongation ofcotton-man-made fibre blends. Pure cotton yarns
Man-made Fibres • Textile Fibre Parameters • fibres and their properties. Textile fibres are used for a wide range of applications such as covering, warmth, personal adornment and even to display personal wealth. Textile technology has come a long way in meeting these requirements. A basic knowledge of textile fibres will facilitate an intelligent appraisal of fibre brands and
The Properties of Man-made Fibres The technical advantages The advantages for the consumer Designation of Man-made Fibres Titre designations Heat-Setting The process The advantages Apparel Manufactured from Man-made Fibres The fabrics The system The functions The Care Properties Handling of textiles The care symbols for textiles The properties of textiles The Significance of Man-made Fibres
This report analyzes the worldwide markets for Cellulosic Man-Made Fibers in Thousand tons. In addition, the Global and the US markets are analyzed by the following Applications: Clothing, Spun Yarn, Fabrics, and Other Applications.
Man-Made Fibres As the name itself indicates these textile fibres are made by man to meet the particular requirements. The chemical composition, structure, and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process.
The main goal of this work was to study the Influence of sportswear fabric properties on the physiological responses and performance of athletes.

