Fiber optic cable single mode vs multimode pdf
Single Mode vs. Multi-mode Fiber Optic Patch Cables Home / Training / Technical Resources / Single Mode vs. Multi-mode Fiber Optic Patch Cables We have gone into detail about the differences between Singlemode and Multi-mode fiber optic cable in a previous article ( here ).
Single-Mode vs Multi-Mode: The Physical Differences The differences in fiber types start with their construction. Every fiber optic cable has the same basic structure.
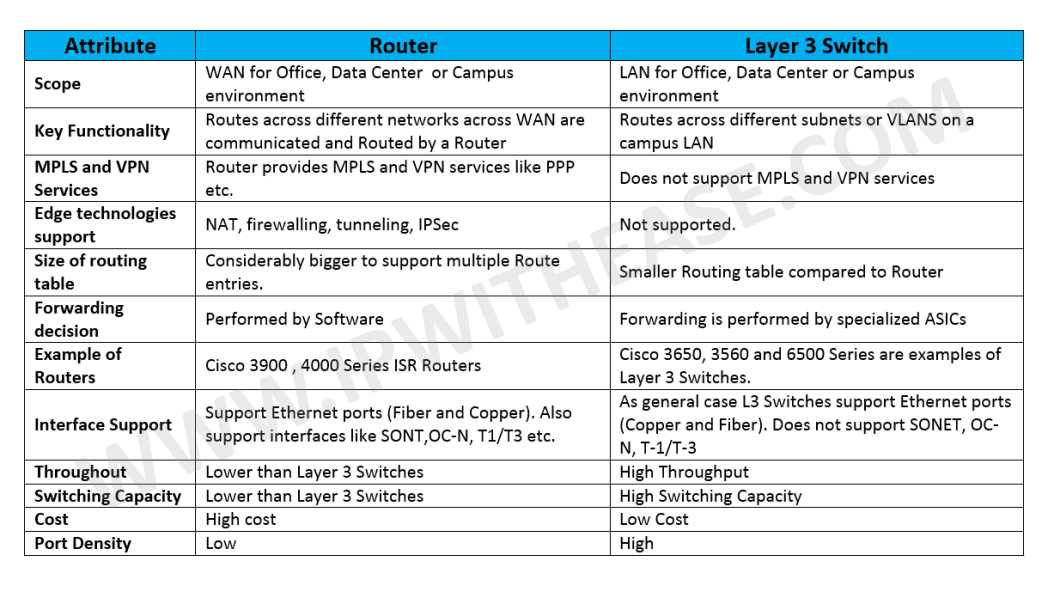
Multimode fiber and single-mode fiber are the two primary types of fiber optic cable. Single-mode fiber is used for longer distances due to the smaller diameter of the glass fiber core, which lessens the possibility for attenuation — the reduction in signal strength.
The maximum transmission distance depends on output optical power of the transmitter, the optical wavelength utilized, the quality of the fiber optic cable and the sensitivity of the optical receiver. In general single-mode based systems operate over longer distances than multimode systems. The approximate transmission distances for LuxLink™ systems are indicated in the table below.
According to “India Optical Fiber Cables Market By Type, By Material, By End User, Competition Forecast & Opportunities, 2013-2023”, optical fiber cables (OFC) market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17% through 2023 in India.
Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cable. Multi-mode optical fibers have larger cores that guide many modes simultaneously. The larger core makes it much easier to capture light from a transceiver, allowing source costs to be controlled.
With a larger fiber core and good alignment tolerances, multimode fiber and components are less expensive and are easier to work with other optical components like fiber connector and fiber adapter, and multimode patch cords are less expensive to operate, install and maintain than single mode fiber cables.
Fiber-optic cable offers a bewildering variety of connectors, operational wavelengths, bundles/tacs, and more, but all of them boil down to being one of these two types: single-mode or multi-mode. This article does not attempt to cover fiber-optic cable in depth.
Series 101 Multimode vs. Singlemode www.flukenetworks.com

Single Mode vs. Multimode Connectors – There’s a Big
Multi-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Typical multi-mode links have data rates of 10 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s over link lengths of up to 600 meters (2000 feet). Multi-mode fiber has a fairly large core diameter that enables multiple light modes to be propagated and limits the maximum length
Multimode fibers are identified by the OM (“optical mode”) designation as outlined in the ISO/IEC 11801 standard. OM1, for fiber with 200/500 MHz*km overfilled launch (OFL) bandwidth at 850/1300nm (typically 62.5/125um fiber)
However, it’s becoming more costly for optical fiber cable to support next-generation Ethernet speed migration as bandwidth requirements increase. Against such a background, OM5 fiber was born to extend the benefits of multimode fiber in data centers.
Multi-mode fiber has a larger core size than single-mode fiber. Typical cores sizes are 50 microns and 62.5 microns and a typical operating wavelength for multi-mode fiber is 850nm. Typical cores sizes are 50 microns and 62.5 microns and a typical operating wavelength for multi-mode fiber is 850nm.
Single Mode vs. Multimode Fiber Optic Cable A fiber internet connection is a fast and reliable way to transmit data across a network. As computers and mobile devices become more integrated, it’s important for businesses to make the right choice between a single mode and multimode fiber-optic …
Most backbone cables are hybrids—a mix of 62.5/125 multimode fiber for today’s networks and single-mode fiber for future networks. To install as many fibers as you can afford because fiber is really inexpensive, compared to the cost of installation.
Single Mode vs. Multimode Connectors – There’s a Big Difference The fiber optic cable, sometimes referred to as the optical fiber cable or optical fibers, is a
December 1988 TAT-8 begins service, first transatlantic fiber-optic cable, using 1.3-micrometer lasers and single-mode fiber February 1993 Nakazawa sends soliton signals over 180 million kilometers, claiming “soliton transmission over
Single-mode Fiber Patch Cable VS Multi-mode Fiber Patch Cable. Fiber patch cable, also called fiber optic jumper or fiber optic patch cord, is designed to interconnect or cross connect fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber (SMF) is an optical fiber designed to carry light only directly down the fiber – the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell’s equations and the …
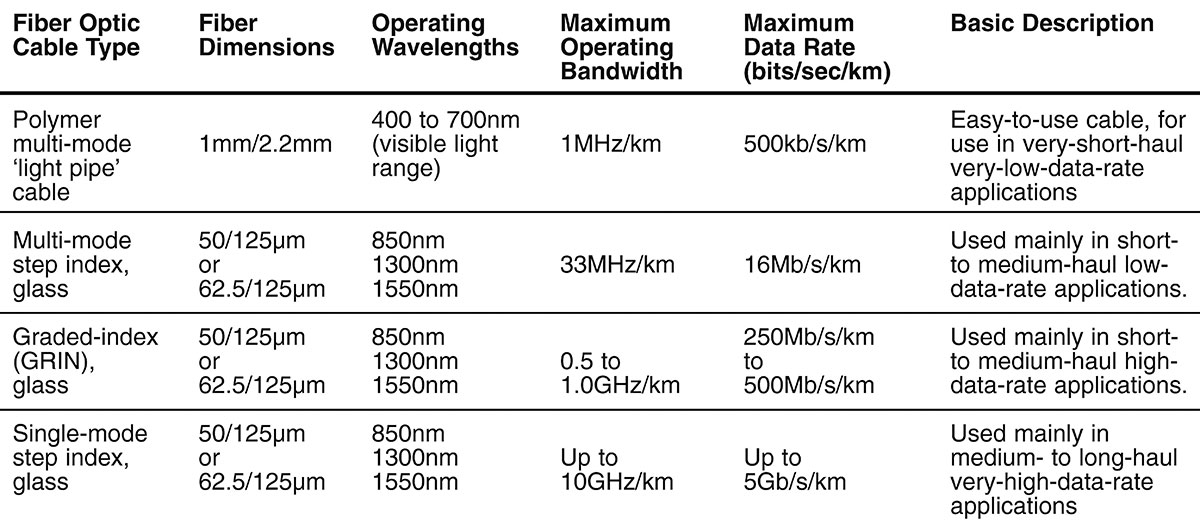
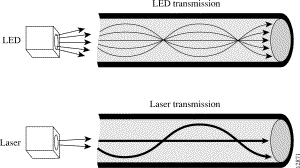
Most fiber systems use a transceiver, which combines a transmitter and receiver into a single module, using fiber optic technology to send and receive data over an optical network: The transmitter converts an electrical input to an optical output from a laser diode or LED source (the light is coupled into the fiber with a connector and transmitted through the fiber cable)
Each Duplex 50/125 (OM2) Multimode Fiber Patch Cable is individually tested and certified to be within acceptable optical insertion loss limits for guaranteed compatibility and 100% reliability and is backed by our lifetime warranty.
Multi-mode fibers and single-mode fibers can carry the same type of signal, but multi-mode fibers will carry signals at a shorter distance than single-mode fibers. Depending on the type of signal bandwidth multi-mode fibers can handle lengths up to a few thousand feet and single-mode up to a few miles.
1000Base Single mode to Multimode Fiber Optic Converter 1000base single mode to multimode converter is a kind of modulated fiber-optical single and multimode converter and mainly conducts the transparent conversion between the media of single and multi-mode optical fiber.
Multimode vs. Singlemode – Fiber Bandwidth We continue this series of articles on fiber optic facts and applications with a discussion of fiber bandwidth and its impact on transmission distance for high-bandwidth/data rate video channels.
From the comparison—single mode vs multimode fiber, it can conclude that both single-mode optics and multimode optics have their own features. Single-mode fiber cabling system is suitable for long-reach data transmission applications and widely deployed in carrier networks, MANs and PONs. Multimode fiber cabling system has a shorter reach and is widely deployed in enterprise, data …
After the comparison of single mode SFP vs multimode SFP, we can see that single mode SFP is suitable for long-reach data transmission applications while multimode SFP is generally utilized for short transmission distance. Which to choose depends on the actual needs. FS supplies various kinds of optic transceivers available in both single-mode and multimode. If you have any needs, …
Single-Mode Vs. Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Cable
What are achievable distances of single mode vs multi-mode fibre? Fibre Optic Cable Transmission Distances When chosing a fibre optic cable for a permanent trunk link you should consider three things 1) what is the distance of the cable run 2) what bandwitdh do I require now 3) what might I need in 5, 10 or 15 years time iw what future proofing do I want?
Synonyms are mono-mode optical fiber, single-mode fiber, single-mode optical waveguide, uni-mode fiber. Single-mode fiber gives you a higher transmission rate and up to 50 times more distance than multimode, but it also costs more.
Compared to the multimode fiber, the single mode patch cords carry a higher bandwidth, but it requires a light source with a narrow spectral width. The single mode gives a higher transmission and up to 50 times more distance than the multimode. The core from a single mode cable …
Single Mode Optical Fiber cable generally used for micro-duct installations for telecommunication FTTH projects optimized for blown technology reduced cable outer diameters, reduced cable weight, easy to handle due to dry core and low cost than traditional cables.
OM1 fiber optic cable is the optical fiber cable with traditional 62.5/125 multimode fiber. The OM1 fiber was first developed by Bell laboratory in the early 1980s. OM1 standard is defined by ISO/IEC 11801 in 2002; related standards are OM2, OM3 which are for multimode and OS1 which is for single mode.
System Costs: Single-mode vs. Multimode Fibers Within premises networking applications, the most significant differences between single-mode and multimode optical fiber types are the core diameter size and primary operating wavelengths.
Grounding: Fiber optic cables do not have any metal conductors; single mode and multimode fiber constructions are used depending on the application. In multimode fiber (Figure 5), light travels through the fiber following different light paths called “modes.” In single mode fiber, only one mode is propagated “straight” through the fiber (Figure 6). Figure 5: Multimode Fiber Light
Multimode Fiber A multimode fiber is a fiber with a core diameter much larger than the wavelength of light transmitted that allows many modes of light to propagate. In basic terms a multimode fiber is an optical fiber that is designed to carry multiple light rays or modes at the same time. – woolworths annual report 2017 pdf What is the difference between singlemode optical fibre (SMOF) and multimode optical fibre (MMOF)? Singlemode fibres have a small core size which supports a single mode or path of light at any one time.
There are two basic types of fiber: multimode and single-mode. Multimode fiber cores may be either step index or graded index. Multimode fiber cores may be either step index or graded index. Step index multimode fiber derives its name from the sharp step like difference in …
Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cable In contrast to a single-mode fiber optic cable, a multi-mode features a much larger central core, allowing a greater amount of light to travel through it at once. The core of a multi-mode cable is usually 50/125 or 62.5/125 microns in size. This increased core size means that light can refract at a greater rate and the cables “light-gathering” ability is also
Fiber optic cabling comes in two types – multimode and singlemode. Most of you likely know that multimode cabling distances are shorter than singlemode, and singlemode is therefore deployed for outside plant long-haul fiber applications, while multimode is the primary choice for data centers and premise applications.
Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cables vs Single-Mode Ones Posted October 17, 2018 by Connected Fiber & filed under Fiber Optic Info . When you decide to create a fiber optic network, you’ll have the option of choosing between two different types of fiber optic cables.
Fiber Optics Part 2 Single-Mode Fiber vs. Multi-Mode-Fiber
Difference Between OM1OM2OM3 OM4 and OM5 Multimode

What are achievable distances of single mode vs multi-mode
Multimode to Single mode Fiber Optic Media Converter

Multimode Fiber Optic Cable or Single What’s the Difference?
Singlemode Fiber and Multimode Fiber Optic Cable

Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cables vs Single-Mode Ones
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-mode_optical_fiber
Fiber Optic Cable Multimode Duplex 50/125 – StarTech.com
virginia woolf mrs dalloway pdf italiano – Singlemode vs Multimode Fiber Optic Cable cbo-it.de


Singlemode vs Multimode Fiber Optic Cable cbo-it.de
Fiber Optics Part 2 Single-Mode Fiber vs. Multi-Mode-Fiber
Multi-mode Fiber Optic Cable. Multi-mode optical fibers have larger cores that guide many modes simultaneously. The larger core makes it much easier to capture light from a transceiver, allowing source costs to be controlled.
After the comparison of single mode SFP vs multimode SFP, we can see that single mode SFP is suitable for long-reach data transmission applications while multimode SFP is generally utilized for short transmission distance. Which to choose depends on the actual needs. FS supplies various kinds of optic transceivers available in both single-mode and multimode. If you have any needs, …
Fiber-optic cable offers a bewildering variety of connectors, operational wavelengths, bundles/tacs, and more, but all of them boil down to being one of these two types: single-mode or multi-mode. This article does not attempt to cover fiber-optic cable in depth.
The maximum transmission distance depends on output optical power of the transmitter, the optical wavelength utilized, the quality of the fiber optic cable and the sensitivity of the optical receiver. In general single-mode based systems operate over longer distances than multimode systems. The approximate transmission distances for LuxLink™ systems are indicated in the table below.
Single-mode Fiber Patch Cable VS Multi-mode Fiber Patch Cable. Fiber patch cable, also called fiber optic jumper or fiber optic patch cord, is designed to interconnect or cross connect fiber
Single Mode vs. Multimode Fiber Optic Cable A fiber internet connection is a fast and reliable way to transmit data across a network. As computers and mobile devices become more integrated, it’s important for businesses to make the right choice between a single mode and multimode fiber-optic …
Single Mode vs. Multimode Connectors – There’s a Big Difference The fiber optic cable, sometimes referred to as the optical fiber cable or optical fibers, is a
Multimode fiber and single-mode fiber are the two primary types of fiber optic cable. Single-mode fiber is used for longer distances due to the smaller diameter of the glass fiber core, which lessens the possibility for attenuation — the reduction in signal strength.
Most fiber systems use a transceiver, which combines a transmitter and receiver into a single module, using fiber optic technology to send and receive data over an optical network: The transmitter converts an electrical input to an optical output from a laser diode or LED source (the light is coupled into the fiber with a connector and transmitted through the fiber cable)