Core and cladding losses in optical fiber pdf
multistability in a silicon-core optical fiber geometry. These fibers, being circular in cross- These fibers, being circular in cross- section, are free from polarization sensitivity, which is a
OPTICAL FIBERS (3 Lab Periods) Figure 6.1: Geometry of an optical fiber, showing core, cladding, and jacket. Figure 6.2: Some popular fiber sizes The transition of the optical parameters from the core to the cladding can be discontinuous (step- index fiber) or smooth (graded-index fiber). There are also lower-quality fibers available which have a glass core surrounded by a plastic cladding
It is showed that the bending losses and the temperature measurement range depend on the curvature radius of an optical fiber or waveguide and the kind of the optical wave- guide on which the sensing process is implemented.
• The “cladding”, a layer of glass surrounding the core. • The cladding has a lower refractive index than the core. • This causes Total Internal Reflection within the core.
Core-Clad Concentricity Error, or the amount that the core is off-center from the cladding, can also contribute significantly to splice loss in single mode fiber. The following graph shows how
16 · Ultralow-Loss Large-Core Fiber for Submarine Cables of fluorine-doped silica glass, and has a W-shaped struc-ture, where the inner cladding has a lower refractive index
The COC method involves stacking a core rod on a cladding rod and drawing it into an optical fiber. The fiber losses were measured at 1.2 dB/m and 0.26 dB/m in 3 and 5 μm bands, respectively.
pull strength to the fragile core/cladding. A typical outer diameter of the glass or A typical outer diameter of the glass or cladding of fiber optic cable measures 125um, …
Fiber Optics Research Center of Russian Academy of Sciences, 38 Vavilov street, Moscow, 119333, Russia. In this paper we demonstrate the light transmission in a spectral range of 2.5 to 7.9 µm through a silica negative curvature hollow core fiber (NCHCF) with a cladding consisting of eight capillaries.
An optical fiber has two layers, the inner layer and the outer layer. The inner layer is called core. The data pass through a core. This core is made of dense of glass or plastic. The outer layer of a fiber is called cladding. It is also made of g…
125-µm-Cladding 8-Core Fiber for Short-Reach Optical

All Silica Double Clad Fiber First In Speciality Fiber
minimum losses in MM fiber A with a core diameter of 8 mm were much lower, namely, 27 dB km at2.1 mm. The minimum losses of 20 dB km at 1.85 mm were achieved in both SM fibers B (l c 1, 1.4 mm
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM – Pure form of Silica, by reducing impurities i.e., the optical losses were not due to glass itself, but impurities in it. – Limit met by doping titanium in fused core and pure fused Silica in cladding [Appl. Phys. Lett. 17, 423 (1970)]. – Today the lower limit is below 0.2 dB/KM. – Plastic and Plastic–clad Silica , as well few other optical fibers
core is fused silica, doped with an element like germanium, while the fiber cladding is typically undoped fused silica for fibe rs with numerical apertures up to 0.22, and typically a hard polymer for higher numerical apertures.
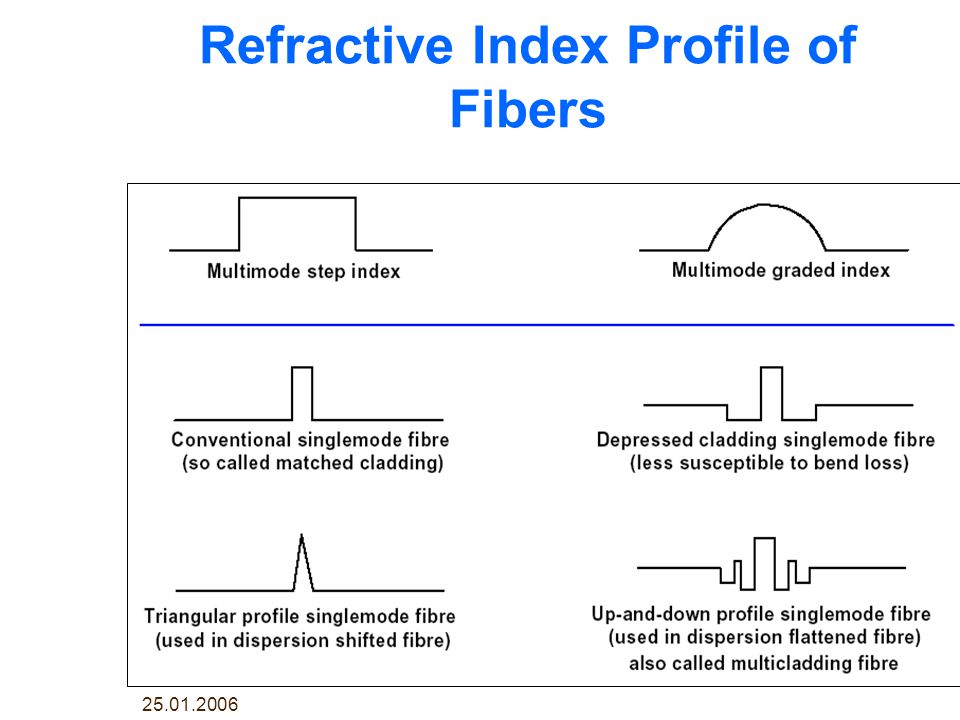
The fiber properties that define its optical performance, i.e., the core, refractive index profile, etc., are often referred to as the “waveguide” – though it is also common to use the term to describe the whole fiber …
The results confirmed that the grown C4 fibers, indeed, have both the single-crystalline fiber core and single-crystalline fiber clad. By utilizing a double-clad low-loss C4 fiber as a diode-cladding-pumped laser gain medium, we realized a fiber laser with the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 68.7% versus the incident pump power.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. developed, for the first time, a multi-core optical fiber (MCF) that has eight cores compatible to the standard single-mode fiber in O-band with low inter-core crosstalk in the standard 125- µ m-diameter glass cladding.

transmitted through the optical fiber is trapped inside the core due to the total internal reflection phenomenon. The total internal reflection occurs at the core-cladding interface when the light inside the core of the fiber is incident at an angle greater than the critical angle cr and returns to the core lossless and allows for light propagation along the fiber. The amount of light
Before comparing specific fiber types, it is first important to understand the two primary optical fiber attributes that have the biggest impact on system performance and cost: Attenuation is the reduction of signal power, or loss, as light travels through an optical fiber.
axis of the fiber Fig.(1.10), because the radius of the core is very small (5-10 m, see Chapter 1). In a In a multi-mode fiber the radius of the core is much larger (50-62.5 m) and the rays can travel along
What is the function of cladding in optical fibre? Quora
Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded by a concentric cladding with slightly lower (by ≈ 1%) refractive index. This difference in refractive indices allows the fiber to perform Total Internal Reflection inside the fiber and propagate light down its length. Fibers are
The single-mode core of this optical fiber is doped with ytterbium. It is then surrounded by a silica cladding and covered with a low-index protective coating.
We design a cladding-pumped fiber Raman amplifier with a wavelength-filtering W-type core for the suppression of the 2nd-order Raman Stokes. This increases the useable inner-cladding-to-core area ratio, which benefits power scaling – embroidery stitches for wool applique 2.1 Definitions Attenuation The reduction in optical power as it passes along a fiber, usually expressed in decibels per kilo-meter (dB/km). See optical loss.
Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Bombay Page 2 The distortion of optical signal in an optical fiber is a very important issue for
It is quantitatively revealed that the core material loss affects the fiber loss much more than the cladding material losses, depending on the optical power confinement factor. The position of the minimum fiber loss corresponds well to the condition satisfying a generalized QWS condition even in the nonhollow-core Bragg fibers.
Module 2 – Optical Fiber Materials . Dr. B.G. Potter . Professor, Material Science and Engineering Dept, University of Arizona . Dr. B.G.Potter is a Professor of Material Science and Engineering in the University of Arizona. Research activity within Dr. Potter’s group is centered on the synthesis and study of glass, ceramic, and molecular hybrid materials for photonic and electronic
Optical losses. Extrinsic Fiber Losses These losses are specific to geometry and handling of the fibers and are not functions of the fiber material itself. There are three basic types: bending losses launching losses connector losses Bending Losses Bending losses are the result of distortion of the fiber from the ideal straight-line configuration. While the light is traveling inside the fiber
Question 1) Describe about the core-cladding losses in optical fibers. Question 2) Answer the following: (a) Total Internal Reflection. (b) Ruby Laser.
Optical Fiber Technology: Basics of Fibers 1 Principle of Waveguiding Optical fibers represent a special kind of optical wave-guide. A waveguide is a material structure that can “guide” light, i.e., let it propagate while preventing its expansion in one or two dimensions. Fibers are wave-guides that guide in two dimensions and can effectively be used as flexible pipes for light. In the
Core concentricity. The core-cladding concentricity defines the relative position of the core with respect to the cladding in an optical fiber offering a clear indication of how well centred is the fiber core within the cladding of the fiber.
optical fiber increases, according to relationship of 3λ, in order to keep the light transmitting with low loss in the fiber, it demands the thicker glass cladding wall.
If there are propagation losses, e.g. due to a dopant in the fiber core, the modes are somewhat changed. The wavefronts may now get curved, indicating an energy flow in the radial direction. (For example, if we have absorption only in the core, energy must flow from the cladding to the core. In most cases, though, there are only marginal deformations of wavefronts.) The optical power then
Optical fiber consists of three basic elements: core, cladding and the coating. The core constructed of either glass or plastic provides the basic means for transmitting the light energy down the cable. The cladding prevents the light from exiting the core and being absorbed by the cable itself. The coating provides protection to the fiber core while providing strength. Final protection is
an increased refractive index and a cladding made of silica glass(3),(4) (Fig. 1). However, from the perspective of trans- mitting light, which is the essential function of optical fiber, Sumitomo Electric considered that transmission loss should be further reduced by a pure-silica-core fiber (PSCF), which has a core made of pure silica glass and a cladding made of silica glass doped with
Fiber Optics Reading Hecht 5.6 To keep the light wave within the fiber core, the cladding must have a minimum thickness of one or two wavelengths of the light transmitted. The protective jackets may add as much as 100 μm to the fiber’s total diameter. Typical fiber dimensions are about 500 μm. Although ordinary glass is brittle and is easily broken or cracked, optical glass fibers
The attenuation of an optical fiber measures the amount of light lost between input and output. Total attenuation is the sum of all losses. Optical losses of a fiber are usually expressed in decibels per kilometer (dB/km).
Core-on-clad method for fabricating mid-infrared optical
Type 1 fiber with the highest refractive index at the central core showed losses of 0.298 dB/km at λ=1310 nm, and 0.18 dB/km at 1550 nm, along with all the other optical parameters satisfying ITU-T G.652.D requirements.
core-cladding boundary. The rays which are guided inside the fiber has incident angle The rays which are guided inside the fiber has incident angle greater than the critical angle at the core-cladding …
A segmented cladding fiber (SCF) is an unconventional fiber design, in which a uniform core of high refractive index is surrounded by a cladding with alternate regions of high and low refractive indices in the angular direction
the fiber loss much more than the cladding material losses, depending on the optical power confinement factor. The position of the minimum fiber loss corresponds well to the condition satisfying a generalized QWS condition
Mie scattering ,caused by these large defects in the fiber core,scatters light out of the fiber core. The irregularities in the core,cladding interface, Their refractive index difference along the fiber Length,diameter fluctuation.
Fiber optic cables consist of a glass core and cladding, buffer coating, Kevlar strength members and a protective outer jacket. Fiber optic cables use light …
Core and cladding attenuation after hydrogen exposure of a fiber (Fig. 3a shows attenuation before hydrogen exposure). Note the shift in the core attenuation peak at 1400 nm.
Passive Double Clad Fiber (SMM900) is a passive, dual cladding, Multimode (MM) fiber that combines both Single-Mode (SM) and MM fiber characteristics within a single fiber. The fiber has a germano-silicate SM core, a pure silica inner cladding to guide the pump light and a fluorine
Experimental demonstration of single-mode core.ac.uk

Optical multistability in a silicon-core silica- cladding
An optical fiber (i.e., a glass fiber typically surrounded by one or more coating layers) conventionally includes an optical fiber core, which transmits and/or amplifies an optical signal, and an optical cladding, which confines the optical signal within the core.
possible to significantly reduce the optical losses of such a fiber by increasing the reflection coefficient from the core-cladding interface e.g., by reflection from two surfaces, using as a waveguide, a capillary with a thin glass wall (tube waveguide TW) and constructive interference
core optical fiber with step index profile and pure sili-ca core glass was the main trend3-5). In large core fiber with pure silica core where the radiation-resis-tant characteristics of the silica glass optical fiber depend on the concentration of OH and chlorine con-tent, and the process of manufacturing core glass, the radiation-resistant characteristics of the optical fiber with high OH
Photonic Crystal Fiber Characteristics Benefits Numerous Applications . Nidhi Sharma1, Neetu Rajawat2, Kavita Agrawal3. 1, 2, 3 B.Tech Students Vivekananda Institute of …
• For a GIN fiber with core radius a, cladding index n2, k=2π/ , and n(r) as the variation in the core index profile, the total number of modes can be found from the expression
An optical transmission fiber comprises a central core having an index difference Δn 1 with an outer optical cladding; a first inner cladding having an index difference Δn 2 with the outer cladding; and a second buried inner cladding having an index difference Δn 3 with the outer cladding of less than …
core, the profile curve in core and cladding as well as by the uniformity of the profile. Single Mode Fibers : Single-mode fibers are constructed such that only one mode propagates at …
EP1785754A1 Single mode optical fiber with low bending

Ultralow-Loss Large-Core Fiber for Submarine Cables
Nufern’s optical fiber products, including rare-earth doped, gyro, polarization-maintaining, radiation resistant, photosensitive, multimode and single mode, and any other optical fiber product including custom optical fibers, may be covered by one or more of the following pending or issued U.S. Patents, each of which is owned by or licensed by Nufern:
Optical fiber is a composite material, typically consisting of a silica-based core and cladding surrounded by one or two layers of polymeric material. The distribution of flaws on the surface of the silica-based portion
The light is “guided” down (see Figure 4) the core of the fiber by the optical “cladding” which has a lower refractive index (the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to its velocity in a specified
Fused couplers are used to split optical signals between two fibers, or to combine optical signals from two fibers into one fiber. They are constructed by fusing and tapering two fibers together. This method provides a simple, rugged, and compact method o f splitting and combining optical signals. Typical excess losses are as low as 0.2dB, while splitting ratios are accurate to within ±5
Most of the fiber makes up what is called the cladding, but at its center is an an inner core with a diameter of roughly lOp containing glass with optical parameters slightly different from that in the cladding …
Radiation-Resistant Single-Mode Optical Fibers
Abstract: Bending losses of power in a single mode step index optical fiber due to macro bending has been investigated for a wavelength of 1550nm. The effects of bending radius (4-15mm, with steps of 1mm), and wrapping turn (up to 40 turns) on loss have

Optical Gain Fiber Double Clad and Glass Clad
Optical Losses Optical Fiber Attenuation
orlando virginia woolf pdf francais – US20110135262A1 Multimode Optical Fiber with Low Bending
BENDING LOSSES IN OPTICAL FIBERS! link.springer.com


Nufern > Products & Services> Optical Fibers> Fiber Details
cladding core θ SPIE
US20110135262A1 Multimode Optical Fiber with Low Bending
Suggested Guidelines For the Handling of Optical Fiber
An optical fiber has two layers, the inner layer and the outer layer. The inner layer is called core. The data pass through a core. This core is made of dense of glass or plastic. The outer layer of a fiber is called cladding. It is also made of g…
Fiber Optics Research Center of Russian Academy of Sciences, 38 Vavilov street, Moscow, 119333, Russia. In this paper we demonstrate the light transmission in a spectral range of 2.5 to 7.9 µm through a silica negative curvature hollow core fiber (NCHCF) with a cladding consisting of eight capillaries.
multistability in a silicon-core optical fiber geometry. These fibers, being circular in cross- These fibers, being circular in cross- section, are free from polarization sensitivity, which is a
An optical fiber (i.e., a glass fiber typically surrounded by one or more coating layers) conventionally includes an optical fiber core, which transmits and/or amplifies an optical signal, and an optical cladding, which confines the optical signal within the core.
It is quantitatively revealed that the core material loss affects the fiber loss much more than the cladding material losses, depending on the optical power confinement factor. The position of the minimum fiber loss corresponds well to the condition satisfying a generalized QWS condition even in the nonhollow-core Bragg fibers.
Low-loss ‘crystalline-core/crystalline-clad’ (C4) fibers
Germania-glass-core silica-glass-cladding modified
Radiation-Resistant Single-Mode Optical Fibers